Crystal structure of pirfenidone (5-methyl-1-phenyl-1 H-pyridin-2-one): an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API)
- PMID: 31392009
- PMCID: PMC6659322
- DOI: 10.1107/S2056989019006418
Crystal structure of pirfenidone (5-methyl-1-phenyl-1 H-pyridin-2-one): an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API)
Abstract
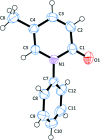
The crystal structure of pirfenidone, C12H11NO [alternative name: 5-methyl-1-phenyl-pyridin-2(1H)-one], an active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) approved in Europe and Japan for the treatment of Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), is reported here for the first time. It was crystallized from toluene by the temperature gradient technique, and crystallizes in the chiral monoclinic space group P21. The phenyl and pyridone rings are inclined to each other by 50.30 (11)°. In the crystal, mol-ecules are linked by C-H⋯O hydrogen bonds involving the same acceptor atom, forming undulating layers lying parallel to the ab plane.
Keywords: active pharmaceutical ingredient (API); crystal structure; hydrogen bonding; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF); pirfenidone.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Crystal structures and the Hirshfeld surface analysis of (E)-4-nitro-N'-(o-chloro, o- and p-methyl-benzyl-idene)benzene-sulfono-hydrazides.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2018 Nov 6;74(Pt 12):1710-1716. doi: 10.1107/S2056989018015207. eCollection 2018 Dec 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2018. PMID: 30574361 Free PMC article.
-
The crystal structures of three pyrazine-2,5-dicarb-oxamides: three-dimensional supra-molecular structures.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 Apr 21;73(Pt 5):729-734. doi: 10.1107/S2056989017005898. eCollection 2017 May 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017. PMID: 28529786 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of N2,N3,N5,N6-tetra-kis-(pyridin-2-ylmeth-yl)pyrazine-2,3,5,6-tetra-carboxamide and N2,N3,N5,N6-tetra-kis-(pyridin-4-ylmeth-yl)pyrazine-2,3,5,6-tetra-carboxamide.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017 Jan 31;73(Pt 2):300-305. doi: 10.1107/S205698901700127X. eCollection 2017 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2017. PMID: 28217363 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structures of N-(pyridin-2-ylmeth-yl)pyrazine-2-carboxamide (monoclinic polymorph) and N-(pyridin-4-ylmeth-yl)pyrazine-2-carboxamide.Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014 Jun 23;70(Pt 7):18-22. doi: 10.1107/S1600536814009519. eCollection 2014 Jul 1. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2014. PMID: 25161497 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure and Hirshfeld surface analysis of the hydro-chloride salt of 8-{4-[(6-phenyl-pyridin-3-yl)meth-yl]piperazin-1-yl}-3,4-di-hydro-quinolin-2(1H)-one.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2021 Jan 29;77(Pt 2):208-212. doi: 10.1107/S2056989021000979. eCollection 2021 Feb 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2021. PMID: 33614156 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
[Pirfenidone inhibits proliferation of rabbit tenon fibroblasts by down-regulating TGF-β3 in the TGF-β/Smad pathway].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Nov 20;41(11):1692-1699. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.11.14. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 34916196 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Solvatomorphism of Moxidectin.Molecules. 2021 Aug 11;26(16):4869. doi: 10.3390/molecules26164869. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34443452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allais, C., Baslé, O., Grassot, J.-M., Fontaine, M., Anguille, S., Rodriguez, J. & Constantieux, T. (2012). Adv. Synth. Catal. 354, 2084–2088.
-
- Bruker (2010). APEX2, SAINT, and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
-
- Crifar, C., Petiot, P., Ahmad, T. & Gagnon, A. (2014). Chem. Eur. J. 20, 2755–2760. - PubMed
-
- Dyachenko, V. D., Butyukova, O. S., Dyachenko, A. D. & Shishkin, O. V. (2011). Zh. Obshch. Khim. 81, 857–868.
-
- Falb, E., Ulanenko, K., Tor, A., Gottesfeld, R., Weitman, M., Afri, M., Gottlieb, H. & Hassner, A. (2017). Green Chem. 19, 5046–5053.
