Radiomics signature for the preoperative assessment of stage in advanced colon cancer
- PMID: 31392079
- PMCID: PMC6682712
Radiomics signature for the preoperative assessment of stage in advanced colon cancer
Abstract
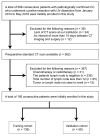
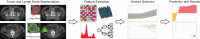
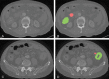
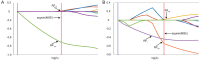
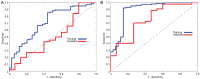
The purpose of this study was to develop a radiomics signature for distinguishing stage in advanced colon cancer (CC). 195 colon cancer patients were enrolled in this study (stage III, n = 146 vs. stage IV, n = 49) and divided into training cohort (n = 136) and validation cohort (n = 59). A total of 286 radiomic features were extracted from tumor and LN images. A radiomics signature was generated using the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) technique. The relationship between radiomics signature and CC staging was explored using a kernel-based support vector machine (SVM) classifier model. The classification performance was assessed by accuracy and the receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curve. A total of 5 features (2 for tumor and 3 for LN) were selected among 286 features. Radiomics signature built from extracted features successfully differentiated stage III from stage IV CC with no known distant metastases on imaging preoperatively. Furthermore, the SVM classifier model generated using tumor and LN images together achieved better performance than the tumor alone, with accuracies of 86.03% vs. 78.68% and 83.05% vs. 76.27% in training and validation cohorts, respectively. In ROC analysis, the model showed a significant improvement for training (AUC 89.16% vs. 69.5%) and validation cohorts (AUC 75.15% vs. 55%) in comparison with the combined analysis and the tumor alone. In conclusion, the radiomics signature based on preoperative CT may distinguish stage III from stage IV CC with no known distant metastases. In addition, the radiomic features from combined images achieved better classification performance than tumor alone.
Keywords: Colon cancer; computed tomography; metastatic lymph node; radiomics; staging.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Magnetic resonance imaging based radiomics signature for the preoperative discrimination of stage I-II and III-IV head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Eur J Radiol. 2018 Sep;106:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2018.07.002. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Eur J Radiol. 2018. PMID: 30150029
-
Magnetic resonance imaging radiomics predicts preoperative axillary lymph node metastasis to support surgical decisions and is associated with tumor microenvironment in invasive breast cancer: A machine learning, multicenter study.EBioMedicine. 2021 Jul;69:103460. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103460. Epub 2021 Jul 4. EBioMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34233259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Computed Tomography-Based Radiomics Model to Predict Central Cervical Lymph Node Metastases in Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Multicenter Study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Oct 21;12:741698. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.741698. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34745008 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics approach for preoperative identification of stages I-II and III-IV of esophageal cancer.Chin J Cancer Res. 2018 Aug;30(4):396-405. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.04.02. Chin J Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30210219 Free PMC article.
-
2-[18F]FDG PET-based quantification of lymph node metabolic heterogeneity for predicting lymph node metastasis in patients with colorectal cancer.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024 May;51(6):1729-1740. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06578-6. Epub 2023 Dec 27. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38150017
Cited by
-
Colorectal liver metastases patients prognostic assessment: prospects and limits of radiomics and radiogenomics.Infect Agent Cancer. 2023 Mar 16;18(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13027-023-00495-x. Infect Agent Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36927442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of KRAS, NRAS and BRAF status in colorectal cancer patients with liver metastasis using a deep artificial neural network based on radiomics and semantic features.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Dec 1;10(12):4513-4526. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33415015 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Assessment and Pancreatic Cancer: Diagnostic Management and Artificial Intelligence.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 5;15(2):351. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020351. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672301 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of therapeutic outcome and survival in a transgenic mouse model of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma treated with dendritic cell vaccination or CDK inhibitor using MRI texture: a feasibility study.Am J Transl Res. 2020 May 15;12(5):2201-2211. eCollection 2020. Am J Transl Res. 2020. PMID: 32509212 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of T Stage of Rectal Cancer After Neoadjuvant Therapy by Multi-Parameter Magnetic Resonance Radiomics Based on Machine Learning Algorithms.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241305463. doi: 10.1177/15330338241305463. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 39668711 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel R, Torre L, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- DeSantis CE, Lin CC, Mariotto AB, Siegel RL, Stein KD, Kramer JL, Alteri R, Robbins AS, Jemal A. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:252–271. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Desantis C, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:104–117. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical practice guidelines in oncology. Colon Cancer. (Version 4) 2018 - PubMed
-
- Ting DT, Ryan DP. The wide gulf between stage III and stage IV colon cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:785–786. - PubMed
