Electrical Impedance Tomography for Cardio-Pulmonary Monitoring
- PMID: 31394721
- PMCID: PMC6722958
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm8081176
Electrical Impedance Tomography for Cardio-Pulmonary Monitoring
Abstract
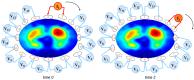
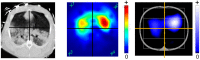
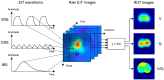
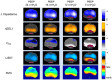
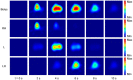
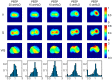
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a bedside monitoring tool that noninvasively visualizes local ventilation and arguably lung perfusion distribution. This article reviews and discusses both methodological and clinical aspects of thoracic EIT. Initially, investigators addressed the validation of EIT to measure regional ventilation. Current studies focus mainly on its clinical applications to quantify lung collapse, tidal recruitment, and lung overdistension to titrate positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP) and tidal volume. In addition, EIT may help to detect pneumothorax. Recent studies evaluated EIT as a tool to measure regional lung perfusion. Indicator-free EIT measurements might be sufficient to continuously measure cardiac stroke volume. The use of a contrast agent such as saline might be required to assess regional lung perfusion. As a result, EIT-based monitoring of regional ventilation and lung perfusion may visualize local ventilation and perfusion matching, which can be helpful in the treatment of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Keywords: bioimpedance; electrical impedance tomography; image reconstruction; monitoring; regional perfusion; regional ventilation; thorax.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Frerichs I., Amato M.B.P., van Kaam A.H., Tingay D.G., Zhao Z., Grychtol B., Bodenstein M., Gagnon H., Böhm S.H., Teschner E., et al. Chest electrical impedance tomography examination, data analysis, terminology, clinical use and recommendations: Consensus statement of the TRanslational EIT developmeNt stuDy group. Thorax. 2017;72:83–93. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2016-208357. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Posada-Quintero H.F., Reljin N., Eaton-Robb C., Noh Y., Riistama J., Chon K.H. Analysis of Consistency of Transthoracic Bioimpedance Measurements Acquired with Dry Carbon Black PDMS Electrodes, Adhesive Electrodes, and Wet Textile Electrodes. Sensors. 2018;18:1719. doi: 10.3390/s18061719. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

