Impact of Graphene Work Function on the Electronic Structures at the Interface between Graphene and Organic Molecules
- PMID: 31394772
- PMCID: PMC6723703
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9081136
Impact of Graphene Work Function on the Electronic Structures at the Interface between Graphene and Organic Molecules
Abstract
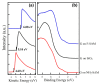
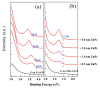
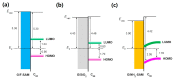
The impact of graphene work function (WF) on the electronic structure at the graphene/organic interface has been investigated. WF manipulation of graphene is realized using self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) with different end groups. With this method, the upper surface of the functionalized graphene remains intact, and thus precludes changes of molecular orientation and packing structures of subsequently deposited active materials. The WF of NH2-SAM functionalized graphene is ~3.90 eV. On the other hand, the WF of graphene increases to ~5.38 eV on F-SAM. By tuning the WF of graphene, an upward band bending is found at the ZnPc/graphene interface on F-SAM. At the interface between C60 and NH2-SAM modified graphene, a downward band bending is observed.
Keywords: band bending; graphene; self-assembled monolayers; work function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Di C.A., Wei D.C., Yu G., Liu Y.Q., Guo Y.L., Zhu D.B. Patterned graphene as source/drain electrodes for bottom-contact organic field-effect transistors. Adv. Mater. 2008;20:3289. doi: 10.1002/adma.200800150. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

