Role of CTCF in DNA damage response
- PMID: 31395350
- PMCID: PMC6690391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2018.02.002
Role of CTCF in DNA damage response
Abstract
CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) is a highly conserved, ubiquitously expressed zinc finger protein. CTCF is a multifunctional protein, associated with a number of vital cellular processes such as transcriptional activation, repression, insulation, imprinting and genome organization. Emerging evidence indicates that CTCF is also involved in DNA damage response. In this review, we focus on the newly identified role of CTCF in facilitating DNA double-strand break repair. Due to the large number of cellular processes in which CTCF is involved, factors that functionally affect CTCF could have serious implications on genomic stability. It is becoming increasingly clear that exposure to environmental toxicants could have adverse effects on CTCF functions. Here we discuss the various ways that environmental toxicants could impact CTCF functions and the potential consequences on DNA damage response.
Keywords: CTCF; Cohesin; DNA double-strand breaks; Environmental toxicants; Nickel; γH2AX.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
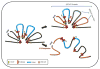
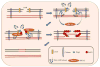

References
-
- De Bont R, van Larebeke N. Endogenous DNA damage in humans: a review of quantitative data. Mutagenesis. 2004;19:169–185. - PubMed
-
- Jackson AL, Loeb LA. The contribution of endogenous sources of DNA damage to the multiple mutations in cancer. Mutat Res. 2001;477:7–21. - PubMed
-
- Cooke MS, Evans MD, Dizdaroglu M, Lunec J. Oxidative DNA damage: mechanisms, mutation, and disease. FASEB J. 2003;17:1195–1214. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

