Radiomic analysis for pretreatment prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer: A multicentre study
- PMID: 31395503
- PMCID: PMC6712288
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.049
Radiomic analysis for pretreatment prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer: A multicentre study
Abstract
Background: We aimed to investigate whether pre-therapeutic radiomic features based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can predict the clinical response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer (LACC).
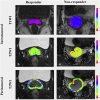
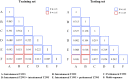
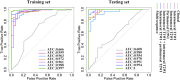
Methods: A total of 275 patients with LACC receiving NACT were enrolled in this study from eight hospitals, and allocated to training and testing sets (2:1 ratio). Three radiomic feature sets were extracted from the intratumoural region of T1-weighted images, intratumoural region of T2-weighted images, and peritumoural region of T2-weighted images before NACT for each patient. With a feature selection strategy, three single sequence radiomic models were constructed, and three additional combined models were constructed by combining the features of different regions or sequences. The performance of all models was assessed using receiver operating characteristic curve.
Findings: The combined model of the intratumoural zone of T1-weighted images, intratumoural zone of T2-weighted images,and peritumoural zone of T2-weighted images achieved an AUC of 0.998 in training set and 0.999 in testing set, which was significantly better (p < .05) than the other radiomic models. Moreover, no significant variation in performance was found if different training sets were used.
Interpretation: This study demonstrated that MRI-based radiomic features hold potential in the pretreatment prediction of response to NACT in LACC, which could be used to identify rightful patients for receiving NACT avoiding unnecessary treatment.
Keywords: Locally advanced cervical cancer; Magnetic resonance imaging; Neoadjuvant chemotherapy; Radiomics.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Multicentric validation of radiomics findings: challenges and opportunities.EBioMedicine. 2019 Sep;47:20-21. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.054. Epub 2019 Aug 29. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 31474549 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Radiomics-Based Pretherapeutic Prediction of Non-response to Neoadjuvant Therapy in Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer.Ann Surg Oncol. 2019 Jun;26(6):1676-1684. doi: 10.1245/s10434-019-07300-3. Epub 2019 Mar 18. Ann Surg Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30887373 Free PMC article.
-
MRI delta radiomics during chemoradiotherapy for prognostication in locally advanced cervical cancer.BMC Cancer. 2025 Jan 22;25(1):122. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13509-1. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 39844102 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics analysis for prediction of lymph node metastasis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy based on pretreatment MRI in patients with locally advanced cervical cancer.Front Oncol. 2024 May 8;14:1376640. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1376640. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38779088 Free PMC article.
-
Multimodal MRI-based deep-radiomics model predicts response in cervical cancer treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2024 Aug 17;14(1):19090. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70055-9. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39154103 Free PMC article.
-
Radiomics-based prediction of two-year clinical outcome in locally advanced cervical cancer patients undergoing neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy.Radiol Med. 2022 May;127(5):498-506. doi: 10.1007/s11547-022-01482-9. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Radiol Med. 2022. PMID: 35325372 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Preoperative Nomogram for Predicting Chemoresistance to Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Patients with Locally Advanced Cervical Squamous Carcinoma Treated with Radical Hysterectomy.Cancer Res Treat. 2021 Jan;53(1):233-242. doi: 10.4143/crt.2020.159. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Cancer Res Treat. 2021. PMID: 32972047 Free PMC article.
-
Value of [18F]FDG PET/CT radiomic parameters in the context of response to chemotherapy in advanced cervical cancer.Sci Rep. 2023 Jun 5;13(1):9092. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-35843-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37277546 Free PMC article.
-
Multiparametric MRI-based radiomic nomogram for predicting HER-2 2+ status of breast cancer.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 27;10(9):e29875. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29875. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38720718 Free PMC article.
-
High-dimensional role of AI and machine learning in cancer research.Br J Cancer. 2022 Mar;126(4):523-532. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01689-z. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Br J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35013580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What benefit can be obtained from magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis with artificial intelligence in prostate cancer compared with clinical assessments?Mil Med Res. 2023 Jun 26;10(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00464-w. Mil Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37357263 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. - PubMed
-
- Bhatla N., Aoki D., Sharma D.N., Sankaranarayanan R. Cancer of the cervix uteri. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2018;143:22–36. - PubMed
-
- DeSouza N.M., Soutter W.P., Rustin G., Mahon M.M., Jones B., Dina R. Use of neoadjuvant chemotherapy prior to radical hysterectomy in cervical cancer: monitoring tumour shrinkage and molecular profile on magnetic resonance and assessment of 3-year outcome. Br J Cancer. 2004;90:2326–2331. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yang Z., Chen D., Zhang J., Yao D., Gao K., Wang H. The efficacy and safety of neoadjuvant chemotherapy in the treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer: a randomized multicenter study. Gynecol Oncol. 2016;141:231–239. - PubMed
-
- Angioli R., Plotti F., Montera R., Aloisi A., Luvero D., Capriglione S. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy plus radical surgery followed by chemotherapy in locally advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2012;127:290–296. - PubMed

