Use and Outcomes of Antiretroviral Monotherapy and Treatment Interruption in Adolescents With Perinatal HIV Infection in Asia
- PMID: 31395514
- PMCID: PMC7007807
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jadohealth.2019.05.025
Use and Outcomes of Antiretroviral Monotherapy and Treatment Interruption in Adolescents With Perinatal HIV Infection in Asia
Abstract
Purpose: Antiretroviral monotherapy and treatment interruption are potential strategies for perinatally HIV-infected adolescents (PHIVA) who face challenges maintaining effective combination antiretroviral therapy (ART). We assessed the use and outcomes for adolescents receiving monotherapy or undergoing treatment interruption in a regional Asian cohort.
Methods: Regional Asian data (2001-2016) were analyzed to describe PHIVA who experienced ≥2 weeks of lamivudine or emtricitabine monotherapy or treatment interruption and trends in CD4 count and HIV viral load during and after episodes. Survival analyses were used for World Health Organization (WHO) stage III/IV clinical and immunologic event-free survival during monotherapy or treatment interruption, and a Poisson regression to determine factors associated with monotherapy or treatment interruption.
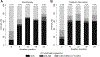
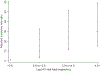
Results: Of 3,448 PHIVA, 84 (2.4%) experienced 94 monotherapy episodes, and 147 (4.3%) experienced 174 treatment interruptions. Monotherapy was associated with older age, HIV RNA >400 copies/mL, younger age at ART initiation, and exposure to ≥2 combination ART regimens. Treatment interruption was associated with CD4 count <350 cells/μL, HIV RNA ≥1,000 copies/mL, ART adverse event, and commencing ART age ≥10 years compared with age <3 years. WHO clinical stage III/IV 1-year event-free survival was 96% and 85% for monotherapy and treatment interruption cohorts, respectively. WHO immunologic stage III/IV 1-year event-free survival was 52% for both cohorts. Those who experienced monotherapy or treatment interruption for more than 6 months had worse immunologic and virologic outcomes.
Conclusions: Until challenges of treatment adherence, engagement in care, and combination ART durability/tolerability are met, monotherapy and treatment interruption will lead to poor long-term outcomes.
Keywords: Adolescent; Antiretroviral therapy; HIV; Monotherapy; Treatment interruption.
Copyright © 2019 Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
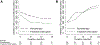
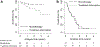
References
-
- Linder V, Goldswain C, Adler H, et al. Lamivudine monotherapy: Experience of medium-term outcomes in HIV-infected children unable to adhere to triple therapy. Pediatr Infect Dis J 2016;35:e199–205. - PubMed
-
- Bunupuradah T, Duong T, Compagnucci A, et al. Outcomes after reinitiating antiretroviral therapy in children randomized to planned treatment interruptions. AIDS 2013;27:579–89. - PubMed
-
- Wainberg MA. The impact of the M184V substitution on drug resistance and viral fitness. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 2004;2:147–51. - PubMed
-
- Wei X, Liang C, Gotte M, Wainberg MA. The M184V mutation in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase reduces the restoration of wild-type replication by attenuated viruses. AIDS 2002;16:2391–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

