Optimal Detection of Subtle Gadolinium Leakage in CSF with Heavily T2-Weighted Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging
- PMID: 31395665
- PMCID: PMC7048436
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A6145
Optimal Detection of Subtle Gadolinium Leakage in CSF with Heavily T2-Weighted Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery Imaging
Abstract
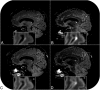
Pericortical enhancement on postcontrast FLAIR images is a marker for subtle leptomeningeal blood-brain barrier leakage. We explored the optimal FLAIR sequence parameters for the detection of low gadolinium concentrations within the CSF. On the basis of phantom experiments and human in vivo data, we showed that detection of subtle pericortical enhancement can be facilitated by using a relatively long TE. Future studies should choose their FLAIR sequence parameters carefully when assessing pericortical enhancement due to subtle blood-brain barrier leakage.
© 2019 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
