Genetic determinants of disease severity in the myotonic dystrophy type 1 OPTIMISTIC cohort
- PMID: 31395669
- PMCID: PMC6745735
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008056
Genetic determinants of disease severity in the myotonic dystrophy type 1 OPTIMISTIC cohort
Erratum in
-
Genetic determinants of disease severity in the myotonic dystrophy type 1 OPTIMISTIC cohort.Neurology. 2020 Mar 10;94(10):459. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008715. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Neurology. 2020. PMID: 32047069 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the role of genetic variation at the DMPK locus on symptomatic diversity in 250 adult, ambulant patients with myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1) recruited to the Observational Prolonged Trial in Myotonic Dystrophy Type 1 to Improve Quality of Life-Standards, a Target Identification Collaboration (OPTIMISTIC) clinical trial.
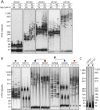
Methods: We used small pool PCR to correct age at sampling biases and estimate the progenitor allele CTG repeat length and somatic mutational dynamics, and AciI digests and repeat primed PCR to test for the presence of variant repeats.
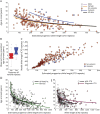
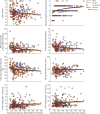
Results: We confirmed disease severity is driven by progenitor allele length, is further modified by age, and, in some cases, sex, and that patients in whom the CTG repeat expands more rapidly in the soma develop symptoms earlier than predicted. We revealed a key role for variant repeats in reducing disease severity and quantified their role in delaying age at onset by approximately 13.2 years (95% confidence interval 5.7-20.7, 2-tailed t test t = -3.7, p = 0.0019).
Conclusions: Careful characterization of the DMPK CTG repeat to define progenitor allele length and presence of variant repeats has increased utility in understanding clinical variability in a trial cohort and provides a genetic route for defining disease-specific outcome measures, and the basis of treatment response and stratification in DM1 trials.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
References
-
- Harper PS. Myotonic Dystrophy. London: WB Saunders; 2001.
-
- Aslanidis C, Jansen G, Amemiya C, et al. . Cloning of the essential myotonic dystrophy region and mapping of the putative defect. Nature 1992;355:548–551. - PubMed
-
- Brook JD, McCurrach ME, Harley HG, et al. . Molecular basis of myotonic dystrophy: expansion of a trinucleotide (CTG) repeat at the 3' end of a transcript encoding a protein kinase family member. Cell 1992;68:799–808. - PubMed
-
- Buxton J, Shelbourne P, Davies J, et al. . Detection of an unstable fragment of DNA specific to individuals with myotonic dystrophy. Nature 1992;355:547–548. - PubMed
-
- Fu YH, Pizzuti A, Fenwick RG, et al. . An unstable triplet repeat in a gene related to myotonic muscular dystrophy. Science 1992;255:1256–1258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
