Bioactive Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Sponge Callyspongia siphonella
- PMID: 31395834
- PMCID: PMC6723499
- DOI: 10.3390/md17080465
Bioactive Brominated Oxindole Alkaloids from the Red Sea Sponge Callyspongia siphonella
Abstract
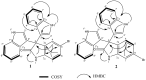
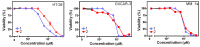
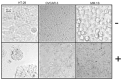
In the present study, LC-HRESIMS-assisted dereplication along with bioactivity-guided isolation led to targeting two brominated oxindole alkaloids (compounds 1 and 2) which probably play a key role in the previously reported antibacterial, antibiofilm, and cytotoxicity of Callyspongia siphonella crude extracts. Both metabolites showed potent antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus (minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) = 8 and 4 µg/mL) and Bacillus subtilis (MIC = 16 and 4 µg/mL), respectively. Furthermore, they displayed moderate biofilm inhibitory activity in Pseudomonas aeruginosa (49.32% and 41.76% inhibition, respectively), and moderate in vitro antitrypanosomal activity (13.47 and 10.27 µM, respectively). In addition, they revealed a strong cytotoxic effect toward different human cancer cell lines, supposedly through induction of necrosis. This study sheds light on the possible role of these metabolites (compounds 1 and 2) in keeping fouling organisms away from the sponge outer surface, and the possible applications of these defensive molecules in the development of new anti-infective agents.
Keywords: Callyspongia siphonella; LC-HRESIMS; antibacterial; antibiofilm; anticancer; antitrypanosomal; metabolomic profiling; oxindole alkaloids; tisindoline.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Hertiani T., Edrada-Ebel R., Ortlepp S., van Soes R.W., de Voogd N.J., Wray V., Hentschel U., Kozytska S., Müller W.E., Proksch P. From anti-fouling to biofilm inhibition: New cytotoxic secondary metabolites from two Indonesian Agelas sponges. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010;18:1297–1311. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2009.12.028. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bergquist P.R. Sponges. University of California Press; Berkeley, CA, USA: 1978.
-
- Ilan M., Gugel J., Van Soest R. Taxonomy, reproduction and ecology of new and known Res Sea Sponges North Atlantic. Mar. Sci. 2004;89:388–410.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

