CMIP is a negative regulator of T cell signaling
- PMID: 31395948
- PMCID: PMC7609264
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-019-0266-5
CMIP is a negative regulator of T cell signaling
Abstract
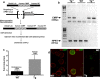
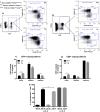
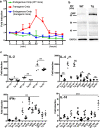
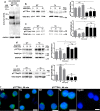
Upon their interaction with cognate antigen, T cells integrate different extracellular and intracellular signals involving basal and induced protein-protein interactions, as well as the binding of proteins to lipids, which can lead to either cell activation or inhibition. Here, we show that the selective T cell expression of CMIP, a new adapter protein, by targeted transgenesis drives T cells toward a naïve phenotype. We found that CMIP inhibits activation of the Src kinases Fyn and Lck after CD3/CD28 costimulation and the subsequent localization of Fyn and Lck to LRs. Video microscopy analysis showed that CMIP blocks the recruitment of LAT and the lipid raft marker cholera toxin B at the site of TCR engagement. Proteomic analysis identified several protein clusters differentially modulated by CMIP and, notably, Cofilin-1, which is inactivated in CMIP-expressing T cells. Moreover, transgenic T cells exhibited the downregulation of GM3 synthase, a key enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of gangliosides. These results suggest that CMIP negatively impacts proximal signaling and cytoskeletal rearrangement and defines a new mechanism for the negative regulation of T cells that could be a therapeutic target.
Keywords: CMIP; T cells; Transgenic mice.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Viola A, Gupta N. Tether and trap: regulation of membrane-raft dynamics by actin-binding proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007;7:889–896. - PubMed
-
- Brownlie RJ, Zamoyska R. T cell receptor signalling networks: branched, diversified and bounded. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013;13:257–269. - PubMed
-
- Sahali D, et al. A novel approach to investigation of the pathogenesis of active minimal- change nephrotic syndrome using subtracted cDNA library screening. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002;13:1238–1247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

