Altered Regional Homogeneity in Patients With Corneal Ulcer: A Resting-State Functional MRI Study
- PMID: 31396034
- PMCID: PMC6664059
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00743
Altered Regional Homogeneity in Patients With Corneal Ulcer: A Resting-State Functional MRI Study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the potential regional homogeneity (ReHo) brain activity changes in patients with corneal ulcer (CU) and their possible relationship with clinical symptoms.
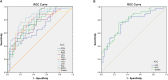
Materials and methods: Forty patients with CU (26 men and 14 women), and 40 healthy controls (HCs) (26 men and 14 women) closely matched in age, sex, and weight underwent resting-state functional MRI scans, respectively. The ReHo method was applied to evaluate synchronous neural activity changes. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC curve) was used to show high test-retest stability and high degree of sensitivity and specificity. We utilized the correlation analysis to calculate the relationship between the average ReHo signal values in different brain areas and the clinical symptoms in CU patients.
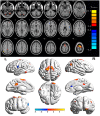
Results: Compared with the HCs, CU patients had significantly increased ReHo values in right cerebellum posterior lobe, left cerebellum posterior lobe, left inferior temporal gyrus, right lingual gyrus, left middle frontal gyrus, left angular gyrus, left cingulate gyrus, right angular gyrus and bilateral superior frontal gyrus, and decreased ReHo values in right anterior cingulate and left precentral gyrus. ROC curve analysis of each brain regions showed the accuracy of AUC was perfect except the right cerebellum posterior lobe. Nevertheless, there was no clear evidence of prominent relevance between the average ReHo values in brain areas and the clinical symptoms.
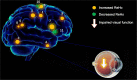
Conclusion: Corneal ulcer caused dysfunctional adaption in different brain areas, which including relatively increased values and decreased values. This finding may help us take a further step in exploring the underlying pathologic mechanisms of CU.
Keywords: brain activity; corneal ulcer; functional MRI; regional homogeneity; resting state.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparison of spontaneous brain activity revealed by regional homogeneity in AQP4-IgG neuromyelitis optica-optic neuritis versus MOG-IgG optic neuritis patients: a resting-state functional MRI study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017 Oct 24;13:2669-2679. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S145183. eCollection 2017. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2017. PMID: 29123400 Free PMC article.
-
Altered spontaneous brain activity in patients with asthma: a resting-state functional MRI study using regional homogeneity analysis.Neuroreport. 2021 Dec 15;32(18):1403-1407. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001736. Neuroreport. 2021. PMID: 34743166
-
Altered regional homogeneity in patients with unilateral acute open-globe injury: a resting-state functional MRI study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016 Aug 1;12:1901-6. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S110541. eCollection 2016. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016. PMID: 27536111 Free PMC article.
-
ALTERED BRAIN ACTIVITY IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC RETINOPATHY USING REGIONAL HOMOGENEITY: A RESTING-STATE fMRI STUDY.Endocr Pract. 2019 Apr;25(4):320-327. doi: 10.4158/EP-2018-0517. Endocr Pract. 2019. PMID: 30995427
-
Altered intrinsic regional spontaneous brain activity in patients with optic neuritis: a resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015 Dec 11;11:3065-73. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S92968. eCollection 2015. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2015. PMID: 26715848 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Guidelines for preoperative visual function and imaging examination standards in vitreoretinal surgery (2025).Int J Ophthalmol. 2025 May 18;18(5):813-831. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2025.05.06. eCollection 2025. Int J Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 40385110 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Brain Activity in Strabismic Amblyopic Children as Determined by Regional Homogeneity: A Resting-State Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 2;16:879253. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.879253. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35720698 Free PMC article.
-
Abnormal Regional Spontaneous Neural Activity in Nonarteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy: A Resting-State Functional MRI Study.Neural Plast. 2020 Sep 9;2020:8826787. doi: 10.1155/2020/8826787. eCollection 2020. Neural Plast. 2020. PMID: 32963518 Free PMC article.
-
Altered brain network centrality in patients with retinal vein occlusion: a resting-state fMRI study.Int J Ophthalmol. 2021 Nov 18;14(11):1741-1747. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2021.11.14. eCollection 2021. Int J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34804865 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Intrinsic Functional Connectivity of the Primary Visual Cortex in Patients with Corneal Ulcer: A Resting-State fMRI Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020 Jun 23;16:1571-1581. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S238463. eCollection 2020. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2020. PMID: 32612359 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

