Sparse Coding Using the Locally Competitive Algorithm on the TrueNorth Neurosynaptic System
- PMID: 31396039
- PMCID: PMC6664083
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00754
Sparse Coding Using the Locally Competitive Algorithm on the TrueNorth Neurosynaptic System
Abstract
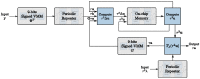
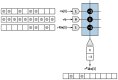
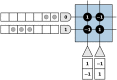
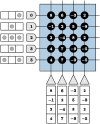
The Locally Competitive Algorithm (LCA) is a biologically plausible computational architecture for sparse coding, where a signal is represented as a linear combination of elements from an over-complete dictionary. In this paper we map the LCA algorithm on the brain-inspired, IBM TrueNorth Neurosynaptic System. We discuss data structures and representation as well as the architecture of functional processing units that perform non-linear threshold, vector-matrix multiplication. We also present the design of the micro-architectural units that facilitate the implementation of dynamical based iterative algorithms. Experimental results with the LCA algorithm using the limited precision, fixed-point arithmetic on TrueNorth compare favorably with results using floating-point computations on a general purpose computer. The scaling of the LCA algorithm within the constraints of the TrueNorth is also discussed.
Keywords: TrueNorth; brain-inspired; sparse-approximation; sparse-code; sparsity; spiking-neurons.
Figures



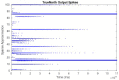
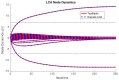
Similar articles
-
A Noise Filtering Algorithm for Event-Based Asynchronous Change Detection Image Sensors on TrueNorth and Its Implementation on TrueNorth.Front Neurosci. 2018 Mar 5;12:118. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00118. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29556172 Free PMC article.
-
Configurable hardware integrate and fire neurons for sparse approximation.Neural Netw. 2013 Sep;45:134-43. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2013.03.012. Epub 2013 Mar 27. Neural Netw. 2013. PMID: 23582485
-
Optimal sparse approximation with integrate and fire neurons.Int J Neural Syst. 2014 Aug;24(5):1440001. doi: 10.1142/S0129065714400012. Epub 2014 Mar 23. Int J Neural Syst. 2014. PMID: 24875786
-
REMODEL: Rethinking Deep CNN Models to Detect and Count on a NeuroSynaptic System.Front Neurosci. 2019 Feb 22;13:4. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00004. eCollection 2019. Front Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30853879 Free PMC article.
-
Computing Generalized Matrix Inverse on Spiking Neural Substrate.Front Neurosci. 2018 Mar 13;12:115. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00115. eCollection 2018. Front Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29593483 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Flash-Based Computing-in-Memory Architecture to Implement High-Precision Sparse Coding.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Nov 30;14(12):2190. doi: 10.3390/mi14122190. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38138359 Free PMC article.
-
Foveal vision reduces neural resources in agent-based game learning.Front Neurosci. 2025 Mar 11;19:1547264. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1547264. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40134416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amir A., Datta P., Risk W. P., Cassidy A. S., Kusnitz J. A., Esser S. K., et al. (2013). Cognitive computing programming paradigm: a Corelet Language for composing networks of neurosynaptic cores, in Proceedings of the 2013 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (Dallas, TX: ), 1–10.
-
- Andreou A. G., Dykman A. A., Fischl K. D., Garreau G., Mendat D. R., Orchard G. M., et al. (2016). Real-time sensory information processing using the TrueNorth neurosynaptic system, in Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS) (Montreal, QC: ), 1–3.
-
- Bahar R. I., Hammerstrom D. W., Harlow J., Joyner W. H., Jr, Lau C., Marculescu D., et al. (2007). Architectures for silicon nanoelectronics and beyond. IEEE Comput. 40, 25–33. 10.1109/MC.2007.7 - DOI
-
- Balavoine A., Rozell C. J., Romberg J. K. (2013a). Convergence of a neural network for sparse approximation using the nonsmooth Łojasiewicz inequality, in Neural Networks (IJCNN), The 2013 International Joint Conference on (IEEE: ), 1–11.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

