Dopamine Receptor Blockade Attenuates Purinergic P2X4 Receptor-Mediated Prepulse Inhibition Deficits and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms
- PMID: 31396053
- PMCID: PMC6664007
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00331
Dopamine Receptor Blockade Attenuates Purinergic P2X4 Receptor-Mediated Prepulse Inhibition Deficits and Underlying Molecular Mechanisms
Abstract
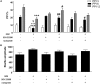
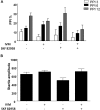
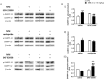
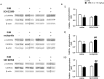
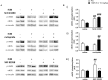
Sensorimotor gating refers to the ability to filter incoming sensory information in a stimulus-laden environment and disruption of this physiological process has been documented in psychiatric disorders characterized by cognitive aberrations. The effectiveness of current pharmacotherapies for treatment of sensorimotor gating deficits in the patient population still remains controversial. These challenges emphasize the need to better understand the biological underpinnings of sensorimotor gating which could lead to discovery of novel drug targets for therapeutic intervention. Notably, we recently reported a role for purinergic P2X4 receptors (P2X4Rs) in regulation of sensorimotor gating using prepulse inhibition (PPI) of acoustic startle reflex. P2X4Rs are ion channels gated by adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP). Ivermectin (IVM) induced PPI deficits in C57BL/6J mice in a P2X4R-specific manner. Furthermore, mice deficient in P2X4Rs [P2X4R knockout (KO)] exhibited PPI deficits that were alleviated by dopamine (DA) receptor antagonists demonstrating an interaction between P2X4Rs and DA receptors in PPI regulation. On the basis of these findings, we hypothesized that increased DA neurotransmission underlies IVM-mediated PPI deficits. To test this hypothesis, we measured the effects of D1 and D2 receptor antagonists, SCH 23390 and raclopride respectively and D1 agonist, SKF 82958 on IVM-mediated PPI deficits. To gain mechanistic insights, we investigated the interaction between IVM and dopaminergic drugs on signaling molecules linked to PPI regulation in the ventral striatum. SCH 23390 significantly attenuated the PPI disruptive effects of IVM to a much greater degree than that of raclopride. SKF 82958 failed to potentiate IVM-mediated PPI disruption. At the molecular level, modulation of D1 receptors altered IVM's effects on dopamine and cyclic-AMP regulated phosphoprotein of 32 kDa (DARPP-32) phosphorylation. Additionally, IVM interacted with the DA receptors antagonists and SKF 82958 in phosphorylation of Ca2+/calmodulin kinase IIα (CaMKIIα) and its downstream target, neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS). Current findings suggest an involvement for D1 and D2 receptors in IVM-mediated PPI disruption via modulation of DARPP-32, CaMKIIα and nNOS. Taken together, the findings suggest that stimulation of P2X4Rs can lead to DA hyperactivity and disruption of information processing, implicating P2X4Rs as a novel drug target for treatment of psychiatric disorders characterized by sensorimotor gating deficits.
Keywords: DARPP-32; P2X4 receptors; dopamine receptors; ivermectin; prepulse inhibition; schizophrenia.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of purinergic P2X4 receptors in regulating striatal dopamine homeostasis and dependent behaviors.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139(1):134-48. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13734. Epub 2016 Aug 15. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27402173 Free PMC article.
-
Reduced expression of purinergic P2X4 receptors increases voluntary ethanol intake in C57BL/6J mice.Alcohol. 2018 May;68:63-70. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2017.09.004. Epub 2017 Sep 30. Alcohol. 2018. PMID: 29477921 Free PMC article.
-
Possible role of the dopamine D1 receptor in the sensorimotor gating deficits induced by high-fat diet.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015 Dec;232(24):4393-400. doi: 10.1007/s00213-015-4068-x. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2015. PMID: 26359228
-
Preclinical evaluation of avermectins as novel therapeutic agents for alcohol use disorders.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018 Jun;235(6):1697-1709. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4869-9. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2018. PMID: 29500584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
P2X4 receptors (P2X4Rs) represent a novel target for the development of drugs to prevent and/or treat alcohol use disorders.Front Neurosci. 2014 Jun 24;8:176. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2014.00176. eCollection 2014. Front Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25009459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Short- and long-term administration of buprenorphine improved gene expression of P2X4 and GABAA receptors in the hippocampus of methamphetamine rats.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 7;8(11):e11432. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11432. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36444255 Free PMC article.
-
Ethanol antagonizes P2X4 receptors in ventral tegmental area neurons.Neuroreport. 2020 Aug 12;31(12):936-941. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001504. Neuroreport. 2020. PMID: 32658126 Free PMC article.
-
To Inhibit or Enhance? Is There a Benefit to Positive Allosteric Modulation of P2X Receptors?Front Pharmacol. 2020 May 12;11:627. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00627. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32477120 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The neurobiological mechanisms and therapeutic prospect of extracellular ATP in depression.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Feb;30(2):e14536. doi: 10.1111/cns.14536. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 38375982 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of P2X4 Receptors to CNS Function and Pathophysiology.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 3;21(15):5562. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155562. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32756482 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Albert K. A., Hemmings H. C., Jr., Adamo A. I., Potkin S. G., Akbarian S., Sandman C. A., et al. (2002). Evidence for decreased DARPP-32 in the prefrontal cortex of patients with schizophrenia. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 59 705–712. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

