A Chinese Herbal Formulation, Xiao-Er-An-Shen Decoction, Attenuates Tourette Syndrome, Possibly by Reversing Abnormal Changes in Neurotransmitter Levels and Enhancing Antioxidant Status in Mouse Brain
- PMID: 31396086
- PMCID: PMC6667554
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00812
A Chinese Herbal Formulation, Xiao-Er-An-Shen Decoction, Attenuates Tourette Syndrome, Possibly by Reversing Abnormal Changes in Neurotransmitter Levels and Enhancing Antioxidant Status in Mouse Brain
Abstract
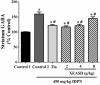
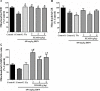
Xiao-Er-An-Shen Decoction (XEASD) has been used clinically for the treatment of Tourette syndrome (TS) in children for more than 20 years in mainland China. The biochemical mechanism underlying the therapeutic action produced by XEASD treatment against TS remains unknown. However, a previous study has shown that pre-incubation of PC12 neuronal cells with XEASD can induce neurite outgrowth and protect against oxidative stress. In the present study, using a mouse model of TS induced by 3,3'-iminodipropionitrile (IDPN), stereotypy scoring, and locomotor activity were assessed. Levels of neurotransmitters including glutamate, aspartate, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in brain tissue as well as plasma cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) were measured using assay kits. The ratio of reduced glutathione (GSH)/oxidized glutathione (GSSG) and Mn-superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) activity in brain mitochondrial fractions as well as mitochondrial glutathione reductase and cytosolic γ-glutamylcysteine activities were also examined. The phosphorylation of cAMP-responsive element binding protein (CREB) in brain tissue was measured by Western blot analysis. XEASD treatment was found to significantly ameliorate the severity of behavioral symptoms in affected mice, as evidenced by decreases in the stereotypy score and locomotor activity. The beneficial effect of XEASD was accompanied by the reversal of abnormal levels of GABA, glutamate, and aspartate, in brain tissue of IDPN-challenged mice. In addition, XEASD treatment increased plasma cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) levels and activated the phosphorylation of CREB in brain tissue of TS mice. Furthermore, XEASD treatment was found to enhance the antioxidant status of brain tissue in affected mice, as evidenced by increases in the GSH/GSSG ratio and the activity of MnSOD in brain mitochondrial fractions. Taken together, these experimental results will hopefully provide insight into the pharmacological basis for the beneficial effects of XEASD in children suffering from TS.
Keywords: Tourette sydrome; Xiao-Er-An-Shen Decoction; antioxidant status; brain; neurotrasmitters.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Chemical characterization and metabolic profiling of Xiao-Er-An-Shen Decoction by UPLC-QTOF/MS.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 2;14:1219866. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1219866. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38027020 Free PMC article.
-
A Chinese Herbal Preparation, Xiao-Er-An-Shen Decoction, Exerts Neuron Protection by Modulation of Differentiation and Antioxidant Activity in Cultured PC12 Cells.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 May 3;2018:8670421. doi: 10.1155/2018/8670421. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 29853977 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of "jian-pi-zhi-dong decoction" on gamma-aminobutyric Acid in a mouse model of tourette syndrome.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:407509. doi: 10.1155/2014/407509. Epub 2014 Apr 9. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24812567 Free PMC article.
-
[Oxidative stress involvement in schizophrenia pathophysiology: a review].Encephale. 2006 Mar-Apr;32(2 Pt 1):244-52. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(06)76151-6. Encephale. 2006. PMID: 16910626 Review. French.
-
Role of selenium toxicity and oxidative stress in aquatic birds.Aquat Toxicol. 2002 Apr;57(1-2):11-26. doi: 10.1016/s0166-445x(01)00263-6. Aquat Toxicol. 2002. PMID: 11879935 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Jian-Pi-Zhi-Dong Decoction on the Amino Acid Neurotransmitters in a Rat Model of Tourette Syndrome and Comorbid Anxiety Disorder.Front Psychiatry. 2020 Jun 5;11:515. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2020.00515. eCollection 2020. Front Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 32581885 Free PMC article.
-
New insights of metabolite abnormalities in the thalamus of rats with iminodiproprionitrile-induced tic disorders.Front Neurosci. 2023 Sep 29;17:1201294. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1201294. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37841690 Free PMC article.
-
Application Potential of Plant-Derived Medicines in Prevention and Treatment of Platinum-Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 13;12:792331. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.792331. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35095502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical characterization and metabolic profiling of Xiao-Er-An-Shen Decoction by UPLC-QTOF/MS.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Nov 2;14:1219866. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1219866. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38027020 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Chemogenetic Inhibition of D1 or D2 Receptor-Containing Neurons of the Substantia Nigra and Striatum in Mice With Tourette Syndrome.Front Mol Neurosci. 2021 Dec 9;14:779436. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2021.779436. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34955745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bajpai V. K., Alam M. B., Quan K. T., Kwon K. R., Ju M. K., Choi H. J., et al. (2017). Antioxidant efficacy and the upregulation of Nrf2-mediated HO-1 expression by (+)-lariciresinol, a lignan isolated from Rubia philippinensis, through the activation of p38. Sci. Rep. 7, 46035. 10.1038/srep46035 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

