Plant Manipulation by Gall-Forming Social Aphids for Waste Management
- PMID: 31396247
- PMCID: PMC6664026
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2019.00933
Plant Manipulation by Gall-Forming Social Aphids for Waste Management
Abstract
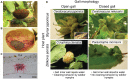
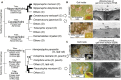
Many social aphids form spectacular galls on their host plants, in which hundreds to thousands of aphids thrive for several months or even for over a year. Here, in addition to colony defense against natural enemies, waste disposal is an important task for the gall dwellers to sustain their social life. In open galls, soldier nymphs actively clean colony wastes such as honeydew droplets, cast-off skins, and cadavers by pushing them with their head out of the gall opening. In the gall, the excreted honeydew is coated with aphid-derived powdery wax to form "honeydew balls," which prevents the aphids from wetting and drowning with their own excretion. How the aphids deal with the accumulated honeydew in closed galls has been a mystery. Here, we report a novel gall-cleaning mechanism: the gall inner surface absorbs and removes the liquid waste through the plant vascular system. Such a plant-mediated water-absorbing property is commonly found in aphids forming closed galls, which must have evolved at least three times independently. By contrast, the inner surface of open galls is wax-coated and water-repelling, and in some cases, the inner surface is covered with dense trichomes, which further enhance the water repellency. In conclusion, gall-forming aphids induce novel plant phenotypes to manage the waste problems by manipulating plant morphogenesis and physiology for their own sake. This review describes our recent studies on waste management strategies by gall-forming social aphids and discusses future directions of this research topic.
Keywords: gall; manipulation; plant cuticle; social aphid; trichome; waste management.
Figures
References
-
- Abbot P., Chapman T. (2017). “Sociality in aphids and thrips” in Comparative social evolution. eds. Rubenstein D. R., Abbot P. (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press; ), 124–153.
-
- Aoki S. (1980). Occurrence of a simple labor in a gall aphid, Pemphigus dorocola (Homoptera, Pemphigidae). Kontyu 48, 71–73.
-
- Aoki S. (1987). “Evolution of sterile soldiers in aphids” in Animal societies: Theories and facts. eds. Ito Y., Brown J. L., Kikkawa J. (Tokyo, Japan: Japan Scientific Societies Press; ), 53–65.
-
- Aoki S., Kurosu U. (1989). Soldiers of Astegopteryx styraci (Homoptera, Aphididoidea) clean their gall. Jpn J. Entomol. 57, 407–416.
-
- Aoki S., Kurosu U. (2010). A review of the biology of Cerataphidini (Hemiptera, Aphididae, Hormaphidinae), focusing mainly on their life cycles, gall formation, and soldiers. Psyche 2010, 1–34. 10.1155/2010/380351 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

