Risk of Malignant Neoplasia with Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 31396537
- PMCID: PMC6664552
- DOI: 10.1155/2019/1534365
Risk of Malignant Neoplasia with Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists are effective glucose-lowering drugs, but there is concern that they may increase the risk of malignant neoplasia. The present meta-analysis examined the safety of GLP-1 receptor agonists with regard to malignant neoplasia.
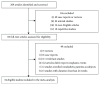
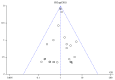
Methods: We analyzed data from randomized controlled trials with a minimum duration of 24 weeks that assessed the incidence of neoplasms in type 2 diabetes patients receiving GLP-1 receptor agonists compared with placebo or other hypoglycemic drugs. We searched the MEDLINE, Embase, and Cochrane databases with a language restriction of English through October 1, 2018, and carried out a meta-analysis of the available trial data using a fixed effects model to calculate odds ratios (ORs) for neoplasia.
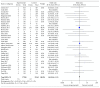
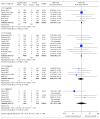
Results: Thirty-four relevant articles, providing data for 50452 patients, were included in the meta-analysis. Compared with the incidence of malignant neoplasia with placebo or other interventions, no increase in malignant neoplasm formation was observed with the use of GLP-1 receptor agonists (OR 1.04, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.94-1.15; p = 0.46), liraglutide (OR 1.08, 95% CI 0.91-1.27; p = 0.38), exenatide (OR 1.00, 95% CI 0.86-1.16; p = 1.00), semaglutide (OR 0.89, 95% CI 0.35-2.22; p = 0.80), or albiglutide (OR 1.07, 95% CI 0.23-4.88; p = 0.93). A subanalysis of trials lasting longer than 3 years also showed no increase in the neoplasia risk with GLP-1 receptor agonist use (OR 1.03, 95% CI 0.92-1.15; p = 0.60). Between-trial statistical heterogeneity was low for all comparisons.
Conclusion: GLP-1 receptor agonists can be used without safety concerns related to malignant neoplasia in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Gier B., Matveyenko A. V., Kirakossian D., Dawson D., Dry S. M., Butler P. C. Chronic GLP-1 receptor activation by exendin-4 induces expansion of pancreatic duct glands in rats and accelerates formation of dysplastic lesions and chronic pancreatitis in the KrasG12D mouse model. Diabetes. 2012;61(5):1250–1262. doi: 10.2337/db11-1109. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

