Prevalence of uncontrolled blood pressure in Meknes, Morocco, and its associated risk factors in 2017
- PMID: 31398197
- PMCID: PMC6688818
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220710
Prevalence of uncontrolled blood pressure in Meknes, Morocco, and its associated risk factors in 2017
Abstract
Background: Uncontrolled high blood pressure (UBP) can lead to various cardiovascular complications causing an estimated nine million deaths per year worldwide. In Meknes, epidemiologic data on UBP are scarce, depriving programs from evidence-based information that would allow a better management of hypertension. Hence, we aimed to assess UBP prevalence in hypertensive patients treated in Meknes and identify UBP-associated risk factors.
Methods: Between November and December 2017, we conducted a cross-sectional study enrolling 922 hypertensive patients managed at Meknes's primary health care facilities using the multistage sampling method. We interviewed patients face to face to collect their socio-demographic-characteristics, lifestyle behaviours, clinical parameters and the triad care system-patient-physician. Another questionnaire was self-administered by physicians to characterize therapeutic inertia. A multivariate logistic regression analysis highlighted the risk factors associated with UBP.
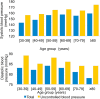
Results: UBP prevalence was 73% with a mean age of 61±11 years (mean±standard deviation) and a male/female ratio of 1/3. Risk factors associated with UBP were: therapeutic inertia (adjusted odds ratio to other variables (AOR) = 18.2, 95% CI [8.35-39.84]), drug non-adherence (AOR = 1.8, 95% CI [1.07-3.04]), obesity/overweight (AOR = 1.6, 95% CI [1.03-2.58]), unemployment (AOR = 1.9, 95% CI [1.09-3.01]), low income (AOR = 2.6, 95% CI [1.01-6.86]), family history of hypertension (AOR = 1.5, 95% CI [1.07-2.08]) and male sex (AOR = 1.6, 95% CI [1.04-2.58]).
Conclusion: UBP prevalence is high in Meknes. Prevention should firstly focus on raised awareness of hypertensive patients' self-care management. Secondly, health professionals should better comply to the guidelines of anti-hypertensive treatments. Lastly, health professionals should frequently be reminded to reach therapeutic goals to overcome therapeutic inertia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Panorama mondial de l'hypertension. Un "tueur silencieux" responsable d'une crise de santé publique mondiale 2013. WHO:[Available from: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/85334/WHO_DCO_WHD_2013.2...
-
- Girerd X, Hanon O, Pannier B, Mourad JJ, Vaisse B. [Determinants of controlled hypertension in patients treated with antihypertensive drugs in France: The French League Against Hypertension Survey (FLAHS 2015)]. Annales de cardiologie et d'angeiologie. 2016;65(3):219–22. 10.1016/j.ancard.2016.04.019 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases