Landscape of Intercellular Crosstalk in Healthy and NASH Liver Revealed by Single-Cell Secretome Gene Analysis
- PMID: 31398325
- PMCID: PMC7262680
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2019.07.028
Landscape of Intercellular Crosstalk in Healthy and NASH Liver Revealed by Single-Cell Secretome Gene Analysis
Abstract
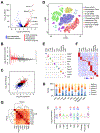
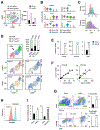
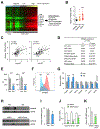
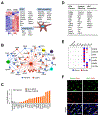
Cell-cell communication via ligand-receptor signaling is a fundamental feature of complex organs. Despite this, the global landscape of intercellular signaling in mammalian liver has not been elucidated. Here we perform single-cell RNA sequencing on non-parenchymal cells isolated from healthy and NASH mouse livers. Secretome gene analysis revealed a highly connected network of intrahepatic signaling and disruption of vascular signaling in NASH. We uncovered the emergence of NASH-associated macrophages (NAMs), which are marked by high expression of triggering receptors expressed on myeloid cells 2 (Trem2), as a feature of mouse and human NASH that is linked to disease severity and highly responsive to pharmacological and dietary interventions. Finally, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) serve as a hub of intrahepatic signaling via HSC-derived stellakines and their responsiveness to vasoactive hormones. These results provide unprecedented insights into the landscape of intercellular crosstalk and reprogramming of liver cells in health and disease.
Keywords: HSC; Kupffer; NAFLD; NASH; NPC; Trem2; liver; macrophage; scRNA-seq; secretome; single-cell; stellakine.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Arendt BM, Comelli EM, Ma DW, Lou W, Teterina A, Kim T, Fung SK, Wong DK, McGilvray I, Fischer SE, et al. (2015). Altered hepatic gene expression in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with lower hepatic n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Hepatology 61, 1565–1578. - PubMed
-
- Clapper JR, Hendricks MD, Gu G, Wittmer C, Dolman CS, Herich J, Athanacio J, Villescaz C, Ghosh SS, Heilig JS, et al. (2013). Diet-induced mouse model of fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis reflecting clinical disease progression and methods of assessment. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 305, G483–495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK098662/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM114160/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK112800/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007863/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001881/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK118731/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007315/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020572/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK034933/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK102456/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM122932/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK117615/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM126917/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

