Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of near-isogenic lines targeting a major 4BL QTL responsible for pre-harvest sprouting in wheat
- PMID: 31399046
- PMCID: PMC6688225
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-019-1961-1
Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of near-isogenic lines targeting a major 4BL QTL responsible for pre-harvest sprouting in wheat
Abstract
Background: Resistance to pre-harvest sprouting (PHS) is one of the major objectives in wheat breeding programs. However, the complex quantitative nature of this trait presents challenges when breeding for PHS resistance. Characterization of PHS using near-isogenic lines (NILs) targeting major quantitative trait locus/loci (QTL/QTLs) can be an effective strategy for the identification of responsible genes and underlying mechanisms.
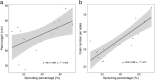
Results: In this study, multiple pairs of NILs were developed and confirmed for a major QTL located on the 4BL chromosome arm that contributes to PHS resistance in wheat, using a combined heterogeneous inbred family method and a fast generation cycling system. Phenotypic characterization of these confirmed NILs revealed significant differences in PHS resistance between the isolines, where the presence of the resistant allele increased the resistance to sprouting on spikes by 54.0-81.9% (average 70.8%) and reduced seed germination by 59.4-70.5% (average 66.2%). The 90 K SNP genotyping assay on the confirmed NIL pairs identified eight SNPs on 4BL, associated with five candidate genes; two of the candidate genes were related to seed dormancy. Agronomic traits in the NIL pairs were investigated; both plant height and grain number per spike were positively correlated with PHS susceptibility.
Conclusions: This study confirmed multiple pairs of NILs and identified SNPs between PHS isolines, which are valuable resources for further fine-mapping of this locus to clone the major genes for PHS resistance and investigate the possible functional regulation of these genes on important agronomic traits, such as plant height and grain number per spike.
Keywords: Grain number per spike; Near-isogenic lines; Plant height; Pre-harvest sprouting; SNP assay; Wheat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic profiling of wheat near-isogenic lines reveals candidate genes on chromosome 3A for pre-harvest sprouting resistance.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jan 21;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02824-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33478384 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association analysis on pre-harvest sprouting resistance and grain color in U.S. winter wheat.BMC Genomics. 2016 Oct 12;17(1):794. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3148-6. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27729004 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of candidate genes, regions and markers for pre-harvest sprouting resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2014 Nov 29;14:340. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0340-1. BMC Plant Biol. 2014. PMID: 25432597 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Improvement of Wheat with Pre-Harvest Sprouting Resistance in China.Genes (Basel). 2023 Mar 30;14(4):837. doi: 10.3390/genes14040837. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37107595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review: Revealing the genetic mechanisms of pre-harvest sprouting in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Plant Sci. 2019 Apr;281:180-185. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.01.004. Epub 2019 Jan 9. Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 30824050 Review.
Cited by
-
Breeding Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) for Pre-Harvest Sprouting Tolerance in South Africa: Current Status and Future Prospects.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jul 10;14(14):2134. doi: 10.3390/plants14142134. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of Candidate Genes for Root Traits Using Genotype-Phenotype Association Analysis of Near-Isogenic Lines in Hexaploid Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 30;22(7):3579. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073579. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33808237 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide association study of drought tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) identifies SNP markers and candidate genes.Mol Genet Genomics. 2024 Mar 2;299(1):22. doi: 10.1007/s00438-024-02104-x. Mol Genet Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38430317 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic profiling of wheat near-isogenic lines reveals candidate genes on chromosome 3A for pre-harvest sprouting resistance.BMC Plant Biol. 2021 Jan 21;21(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12870-021-02824-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33478384 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Characterization of Near-Isogenic Lines Revealing Candidate Genes for a Major 7AL QTL Responsible for Heat Tolerance in Wheat.Front Plant Sci. 2020 Aug 28;11:1316. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2020.01316. eCollection 2020. Front Plant Sci. 2020. PMID: 32983205 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Biddulph T, Plummer J, Setter T, Mares D. Seasonal conditions influence dormancy and preharvest sprouting tolerance of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in the field. Field Crop Res. 2008;107(2):116–128. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2008.01.003. - DOI
-
- Biddulph T. Mechanisms of dormancy, preharvest sprouting tolerance and how they are influenced by the environment during grain filling and maturation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) Perth: The University of Western Australia; 2006.
-
- Darabi H, Mohandessi S, Balavar Y, Moghaddam M, Aghapoor K, Mohsenzadeh F, Nourinia A. Clove bud oil: an efficient, economical and widely available oil for the inhibition of wheat seed germination. Environ Chem Lett. 2011;9(4):519–524. doi: 10.1007/s10311-011-0312-8. - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

