Complement activation products in the circulation and urine of primary membranous nephropathy
- PMID: 31399080
- PMCID: PMC6688252
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-019-1509-5
Complement activation products in the circulation and urine of primary membranous nephropathy
Abstract
Background: Complement activation plays a substantial role in the pathogenesis of primary membranous nephropathy (pMN). C5b-9, C3c, MBL, and factor B have been documented in the subepithelial immune deposits. However, the changing of complement activation products in circulation and urine is not clear.
Methods: We measured the circulating and urinary levels of C1q, MBL, C4d, Bb, properdin, C3a, C5a, and sC5b-9, in 134 patients with biopsy-proven pMN, by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. All the plasma values were corrected by eGFR and all the urinary values were corrected by urinary creatinine and urinary protein excretion. Anti-PLA2R antibodies were measured in all patients.
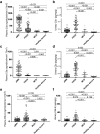
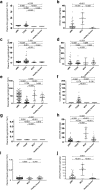
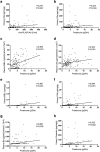
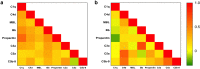
Results: The plasma complement activation products were elevated both in the patients with and without anti-PLA2R antibodies. C3a levels were remarkably increased in the circulation and urine, much higher than the elevated levels of C5a. C5b-9 was in normal range in plasma, but significantly higher in urine. The urinary C5a had a positive correlation with anti-PLA2R antibody levels and urinary protein. The plasma level of C4d was elevated, but C1q and MBL were comparable to healthy controls. Positive correlations were observed between plasma C4d/MBL and urinary protein, only in the patients with positive anti-PLA2R antibodies but not in those without. The plasma level of Bb was elevated and had positive correlation with urinary protein only in the patients without anti-PLA2R antibodies.
Conclusion: Complement activation products were remarkable increased in pMN and may serve as sensitive biomarkers of disease activity. The complement may be activated through lectin pathway with the existence of anti-PLA2R antibodies, while through alternative pathway in the absence of antibody.
Keywords: C3a; C5a; Complement; PLA2R; Primary membranous nephropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of serum mannose-binding lectin, anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody and renal outcomes in idiopathic membranous nephropathy and atypical membranous nephropathy: a single center retrospective cohort study.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):428-433. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2048016. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35272568 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship of anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody and C5a complement with disease activity and short-term outcome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy.J Formos Med Assoc. 2019 May;118(5):898-906. doi: 10.1016/j.jfma.2018.12.026. Epub 2019 Jan 11. J Formos Med Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30639075
-
Complement Alternative Pathway׳s Activation in Patients With Lupus Nephritis.Am J Med Sci. 2017 Mar;353(3):247-257. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.01.005. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Am J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28262211
-
The role of complement in membranous nephropathy.Semin Nephrol. 2013 Nov;33(6):531-42. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2013.08.004. Semin Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 24161038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunology of membranous nephropathy: from animal models to humans.Clin Exp Immunol. 2016 Feb;183(2):157-65. doi: 10.1111/cei.12729. Epub 2015 Nov 24. Clin Exp Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26459770 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of serum mannose-binding lectin, anti-phospholipase A2 receptor antibody and renal outcomes in idiopathic membranous nephropathy and atypical membranous nephropathy: a single center retrospective cohort study.Ren Fail. 2022 Dec;44(1):428-433. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2022.2048016. Ren Fail. 2022. PMID: 35272568 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Complement Pathway Activation in Autoimmune Glomerulonephritis.Kidney Int Rep. 2022 Feb 14;7(5):1027-1036. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2022.02.002. eCollection 2022 May. Kidney Int Rep. 2022. PMID: 35571000 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of complement serum C3 level and glomerular C3 deposits in anti-glomerular basement membrane disease.Front Immunol. 2023 Jul 5;14:1190394. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1190394. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37475859 Free PMC article.
-
Urinary complement biomarkers in immune-mediated kidney diseases.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 3;15:1357869. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1357869. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38895123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of Primary Membranous Nephropathy.Biomolecules. 2021 Mar 30;11(4):513. doi: 10.3390/biom11040513. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 33808418 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Behnert A, Schiffer M, Muller-Deile J, Beck LH, Jr, Mahler M, Fritzler MJ. Antiphospholipase a (2) receptor autoantibodies: a comparison of three different immunoassays for the diagnosis of idiopathic membranous nephropathy. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:143274. doi: 10.1155/2014/143274. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Espinosa-Hernandez M, Ortega-Salas R, Lopez-Andreu M, Gomez-Carrasco JM, Perez-Saez MJ, Perez-Seoane C, Aljama-Garcia P. C4d as a diagnostic tool in membranous nephropathy. Nefrologia. 2012;32(3):295–299. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

