Eosinophilic esophagitis in children: doubts and future perspectives
- PMID: 31399124
- PMCID: PMC6688237
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-019-2014-0
Eosinophilic esophagitis in children: doubts and future perspectives
Abstract
Background: Eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) is a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disorder and represents the leading cause of food impaction. The pathogenesis of EoE is the result of an interplay between genetic, environmental and host immune system factors. New therapeutic approaches for EoE have been proposed. In this manuscript we review the current evidence regarding EoE management in pediatric age, with a particular focus on new findings related to the efficacy and safety of monoclonal antibodies.
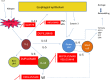
Main body: Conventional therapies have failed in treating some patients with EoE, which then requires aggressive procedures such as esophageal dilatation. The most effective available medical therapy for EoE is swallowed topic corticosteroids (fluticasone propionate and budesonide), which have two main drawbacks: they are related to well-known adverse effects (especially in the paediatric population), and there are not enough long-term data to confirm that they are able to reverse the remodelling process of the esophageal mucosa, which is the major cause of EoE symptoms (including dysphagia, abdominal pain, nausea, obstruction, perforation and vomiting). The monoclonal antibodies appear to be an interesting therapeutic approach. However, the studies conducted until now have shown substantial histological improvement not coupled with significant clinical improvements and no significant relationship between a decreasing number of eosinophils and clinical symptoms, highlighting the importance in the pathogenesis of EoE of cells such as T-helper cells, mast cells, B cells, epithelial cells and natural killer cells.
Conclusions: Monoclonal antibodies targeting a signal involved in the pathogenesis of EoE may not break the complex self-propagating inflammatory activation responsible for perpetuation of the inflammatory response and the development of symptoms and complications. We speculate that combined biological therapies targeting more than one molecule or cell may provide better results, with conventional therapies potentially enhancing the effects of antibodies. However, further studies should aim to find the best therapeutic approach to target the cells involved in the remodelling process and to reverse the histological changes in this complex clinical condition.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Dysphagia; Eosinophilic esophagitis; Esophageal symptoms; Food allergy; Monoclonal antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, von Arnim U, Bredenoord AJ, Bussmann C, Amil Dias J, Bove M, González-Cervera J, Larsson H, Miehlke S, Papadopoulou A, Rodríguez-Sánchez J, Ravelli A, Ronkainen J, Santander C, Schoepfer AM, Storr MA, Terreehorst I, Straumann A, Attwood SE. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. United European Gastroenterol J. 2017;5:335–358. doi: 10.1177/2050640616689525. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dellon ES, Gibbs WB, Fritchie KJ, Rubinas TC, Wilson LA, Woosley JT, Shaheen NJ. Clinical, endoscopic, and histologic findings distinguish eosinophilic esophagitis from gastroesophageal reflux disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2009;7:1305–1313. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2009.08.030. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

