c-Abl-Mediated Tyrosine Phosphorylation of PARP1 Is Crucial for Expression of Proinflammatory Genes
- PMID: 31399520
- PMCID: PMC6731455
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1801616
c-Abl-Mediated Tyrosine Phosphorylation of PARP1 Is Crucial for Expression of Proinflammatory Genes
Abstract
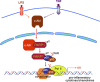
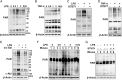
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is a rapid and transient posttranslational protein modification mostly catalyzed by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP1). Fundamental roles of activated PARP1 in DNA damage repair and cellular response pathways are well established; however, the precise mechanisms by which PARP1 is activated independent of DNA damage, and thereby playing a role in expression of inflammatory genes, remain poorly understood. In this study, we show that, in response to LPS or TNF-α exposure, the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase c-Abl undergoes nuclear translocation and interacts with and phosphorylates PARP1 at the conserved Y829 site. Tyrosine-phosphorylated PARP1 is required for protein poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation of RelA/p65 and NF-κB-dependent expression of proinflammatory genes in murine RAW 264.7 macrophages, human monocytic THP1 cells, or mouse lungs. Furthermore, LPS-induced airway lung inflammation was reduced by inhibition of c-Abl activity. The present study elucidated a novel signaling pathway to activate PARP1 and regulate gene expression, suggesting that blocking the interaction of c-Abl with PARP1 or pharmaceutical inhibition of c-Abl may improve the outcomes of PARP1 activation-mediated inflammatory diseases.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Association of Immunologists, Inc.
Figures








References
-
- Schreiber V., Dantzer F., Ame J. C., de Murcia G. 2006. Poly(ADP-ribose): novel functions for an old molecule. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7: 517–528. - PubMed
-
- Malanga M., Althaus F. R. 2005. The role of poly(ADP-ribose) in the DNA damage signaling network. Biochem. Cell Biol. 83: 354–364. - PubMed
-
- Haince J. F., McDonald D., Rodrigue A., Déry U., Masson J. Y., Hendzel M. J., Poirier G. G. 2008. PARP1-dependent kinetics of recruitment of MRE11 and NBS1 proteins to multiple DNA damage sites. J. Biol. Chem. 283: 1197–1208. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

