Artificial intelligence in digital pathology - new tools for diagnosis and precision oncology
- PMID: 31399699
- PMCID: PMC6880861
- DOI: 10.1038/s41571-019-0252-y
Artificial intelligence in digital pathology - new tools for diagnosis and precision oncology
Abstract
In the past decade, advances in precision oncology have resulted in an increased demand for predictive assays that enable the selection and stratification of patients for treatment. The enormous divergence of signalling and transcriptional networks mediating the crosstalk between cancer, stromal and immune cells complicates the development of functionally relevant biomarkers based on a single gene or protein. However, the result of these complex processes can be uniquely captured in the morphometric features of stained tissue specimens. The possibility of digitizing whole-slide images of tissue has led to the advent of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning tools in digital pathology, which enable mining of subvisual morphometric phenotypes and might, ultimately, improve patient management. In this Perspective, we critically evaluate various AI-based computational approaches for digital pathology, focusing on deep neural networks and 'hand-crafted' feature-based methodologies. We aim to provide a broad framework for incorporating AI and machine learning tools into clinical oncology, with an emphasis on biomarker development. We discuss some of the challenges relating to the use of AI, including the need for well-curated validation datasets, regulatory approval and fair reimbursement strategies. Finally, we present potential future opportunities for precision oncology.
Figures

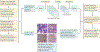
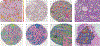

References
-
- Prewitt JMS Intelligent microscopes: recent and near-future advances. Proc. SPIE 10.1117/12.958214 (1979). - DOI
-
- Prewitt JMS Parametric and nonparametric recognition by computer: an application to leukocyte image processing. Adv. Comput. 12, 285–414 (1972).
-
- Prewitt JMS & Mendelsohn ML The analysis of cell images. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 128, 1035–1053 (1966). - PubMed
-
- McCarthy J, Minsky ML, Rochester N & Shannon CE A proposal for the Dartmouth summer research project on artificial intelligence, August 31, 1955 AI Mag. 27, 12 (2006).
-
- McCarthy JJ, Minsky ML & Rochester N Artificial intelligence. Research Laboratory of Electronics (RLE) at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) https://dspace.mit.edu/handle/1721.1/52263 (1959).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

