Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of haemorrhoidal disease: a minimally invasive and effective treatment modality
- PMID: 31399891
- PMCID: PMC6736898
- DOI: 10.1007/s10151-019-02054-2
Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of haemorrhoidal disease: a minimally invasive and effective treatment modality
Abstract
Background: Haemorrhoidal disease (HD) is a common colorectal condition that often requires surgical treatment. Less invasive procedures are usually more acceptable to patients. The aim of this study was to report the outcome of a novel and minimally invasive technique employing a radiofrequency ablation (RFA) energy (Rafaelo®) to treat HD.
Methods: A total number of 27 patients who had RFA for the treatment of HD were recruited to this study. The procedure was performed under deep sedation and local anaesthesia. Patients' demographics; haemorrhoid severity score (HSS); quality of life; pain and satisfaction scores; and recurrence rate were recorded.
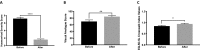
Results: The mean age of the patients was 46 (SD 14) years, 18 (67%) males and 9 (33%) females. The mean body mass index was 25 (SD 4) kg/m2. The predominant symptom of all patients was per-rectal bleeding. HSS improved from 7.2 (SD 1.9) before the procedure to 1.6 (SD 1) after the procedure (p < 0.0001). Postoperative pain scores on a scale of 0-10 were 0, 2 (SD 2), 1 (SD 2), and 0 on immediate, day-1, day-3, and 2-month follow-up questionnaire. The mean satisfacion score was 9 (SD 1.5) out of 10 on 2-month follow-up. Mean time until patients returned to normal daily activity was 3 (SD 1) days following the procedure. Quality-of-life assessments including: visual analogue scale scores (before: mean 70, SD 23; after: mean 82, SD 16; p < 0.001) and EQ-5D-5L (before: mean 0.84, SD 0.15; after: mean 0.94, SD 0.13; p < 0.05) were significantly improved. The mean length of follow-up for recurrence of symptoms was 20 months (range 12-32 months). One patient (4%) reported the recurrence of rectal bleeding 12 months after the procedure.
Conclusions: RFA for the treatment of HD is safe and effective in achieving symptomatic relief. It is associated with minimal postoperative pain and low incidence of recurrence.
Keywords: Hemorrhoids; Minimally invasive surgical procedures; Patient reported outcome; Radiofrequency ablation.
Conflict of interest statement
Modern Aesthetic Solutions Ltd (Registered Office: 39 Steeple Close, Poole, Dorset BH17 9B) has provided the Rafaelo® radio frequency device as a loan for 5 years to the University College London Hospital and funded the cost of Rafaelo® specific equipment for the initial 10 patients who underwent radiofrequency ablation of haemorrhoids. Furthermore, Modern Aesthetic Solution Ltd continues to sponsor a biannual live link course at University College London Hospital to teach radiofrequency ablation for haemorrhoids to other surgeons.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Early and midterm results of radiofrequency ablation (Rafaelo® procedure) for third-degree haemorrhoids: a prospective, two-centre study.Tech Coloproctol. 2022 Jun;26(6):479-487. doi: 10.1007/s10151-022-02608-x. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Tech Coloproctol. 2022. PMID: 35305182 Free PMC article.
-
French multicentre prospective evaluation of radiofrequency ablation in the management of haemorrhoidal disease.Tech Coloproctol. 2023 Oct;27(10):873-883. doi: 10.1007/s10151-023-02787-1. Epub 2023 Apr 2. Tech Coloproctol. 2023. PMID: 37005961 Free PMC article.
-
HAL-RAR (Doppler guided haemorrhoid artery ligation with recto-anal repair) is a safe and effective procedure for haemorrhoids. Results of a prospective study after two-years follow-up.Int J Surg. 2016 Apr;28:39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.02.030. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Int J Surg. 2016. PMID: 26876958 Review.
-
Hemorrhoidal ablation and fixation: an alternative procedure for prolapsing hemorrhoids.Digestion. 2005;72(2-3):181-8. doi: 10.1159/000088457. Epub 2005 Sep 20. Digestion. 2005. PMID: 16179786
-
Transanal hemorrhoidal dearterialization (THD) for hemorrhoidal disease: a single-center study on 1000 consecutive cases and a review of the literature.Tech Coloproctol. 2017 Dec;21(12):953-962. doi: 10.1007/s10151-017-1726-5. Epub 2017 Nov 24. Tech Coloproctol. 2017. PMID: 29170839 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Radiofrequency thermocoagulation of haemorrhoids: learning curve of a novel approach.J Surg Case Rep. 2023 Mar 17;2023(3):rjad115. doi: 10.1093/jscr/rjad115. eCollection 2023 Mar. J Surg Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36937798 Free PMC article.
-
Initial experience of radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of advanced haemorrhoidal disease.Prz Gastroenterol. 2022;17(3):234-239. doi: 10.5114/pg.2021.110011. Epub 2021 Oct 14. Prz Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36127948 Free PMC article.
-
Early and midterm results of radiofrequency ablation (Rafaelo® procedure) for third-degree haemorrhoids: a prospective, two-centre study.Tech Coloproctol. 2022 Jun;26(6):479-487. doi: 10.1007/s10151-022-02608-x. Epub 2022 Mar 19. Tech Coloproctol. 2022. PMID: 35305182 Free PMC article.
-
What can patients expect in the long term from radiofrequency thermocoagulation of hemorrhoids on bleeding, prolapse, quality of life, and recurrence: "no pain, no gain" or "no pain but a gain"?Ann Coloproctol. 2024 Oct;40(5):481-489. doi: 10.3393/ac.2022.00311.0044. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Ann Coloproctol. 2024. PMID: 36217810 Free PMC article.
-
Still a Case of "No Pain, No Gain"? An Updated and Critical Review of the Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Management Options for Hemorrhoids in 2020.Ann Coloproctol. 2020 Jun;36(3):133-147. doi: 10.3393/ac.2020.05.04. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Ann Coloproctol. 2020. PMID: 32674545 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brown SR, Tiernan JP, Watson AJ, et al. Haemorrhoidal artery ligation versus rubber band ligation for the management of symptomatic second-degree and third-degree haemorrhoids (HubBLe): a multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2016;388(10042):356–364. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30584-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gupta PJ. Novel technique: radiofrequency coagulation—a treatment alternative for early-stage hemorrhoids. Med Gen Med. 2002;4(3):1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

