Antifibrotic Roles of RAAS Blockers: Update
- PMID: 31399990
- PMCID: PMC7121580
- DOI: 10.1007/978-981-13-8871-2_33
Antifibrotic Roles of RAAS Blockers: Update
Abstract
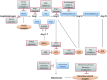
The rennin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) has been well documented in regulating blood pressure, fluid volume, and sodium balance. Overactivity of RAAS promotes both systemic and regional glomerular capillary hypertension, which could induce hemodynamic injury to the glomerulus, leading to kidney damage and renal fibrosis via profibrotic and proinflammatory pathway. Therefore, the use of RAAS inhibitors (i.e., ACEIs, ARBs, and MRAs) as the optional therapy has been demonstrated to prevent proteinuria, and kidney fibrosis and slow the decline of renal function effectively in the process of kidney disease during the last few decades. Recently, several new components of the RAAS have been discovered, including ACE2 and the corresponding ACE2/Ang (1-7)/Mas axis, which are also present in the kidney. Besides the classic RAAS inhibitors target the angiotensin-AT1-aldosterone axis, with the expanding knowledge about RAAS, a number of potential therapeutic targets in this system is emerging. Newer agents that are more specific are being developed. The present chapter outlines the insights of the RAAS agents (classic RAAS antagonists/the new RAAS drugs), and discusses its clinical application in the combat of renal fibrosis.
Keywords: Antagonists; Fibrosis; Renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system (RAAS).
Figures
References
-
- Andersen K, Hartman D, Peppard T, Hermann D, Van Ess P, Lefkowitz M, et al. The effects of aldosterone synthase inhibition on aldosterone and cortisol in patients with hypertension: a phase II, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter study. J Clin Hypertens. 2012;14:580–587. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-7176.2012.00667.x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arai K, Morikawa Y, Ubukata N, Tsuruoka H, Homma T. CS-3150, a novel nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, shows preventive and therapeutic effects on renal injury in deoxycorticosterone acetate/salt-induced hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2016;358:548–557. doi: 10.1124/jpet.116.234765. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous