CEST MR-Fingerprinting: Practical considerations and insights for acquisition schedule design and improved reconstruction
- PMID: 31400034
- PMCID: PMC7190069
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.27937
CEST MR-Fingerprinting: Practical considerations and insights for acquisition schedule design and improved reconstruction
Abstract
Purpose: To understand the influence of various acquisition parameters on the ability of CEST MR-Fingerprinting (MRF) to discriminate different chemical exchange parameters and to provide tools for optimal acquisition schedule design and parameter map reconstruction.
Methods: Numerical simulations were conducted using a parallel computing implementation of the Bloch-McConnell equations, examining the effect of TR, TE, flip-angle, water and , saturation-pulse duration, power, and frequency on the discrimination ability of CEST-MRF. A modified Euclidean distance matching metric was evaluated and compared to traditional dot product matching. L-Arginine phantoms of various concentrations and pH were scanned at 4.7T and the results compared to numerical findings.
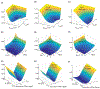
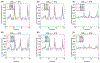
Results: Simulations for dot product matching demonstrated that the optimal flip-angle and saturation times are and 1100 ms, respectively. The optimal maximal saturation power was 3.4 μT for concentrated solutes with a slow exchange rate, and 5.2 μT for dilute solutes with medium-to-fast exchange rates. Using the Euclidean distance matching metric, much lower maximum saturation powers were required (1.6 and 2.4 μT, respectively), with a slightly longer saturation time (1500 ms) and flip-angle. For both matching metrics, the discrimination ability increased with the repetition time. The experimental results were in agreement with simulations, demonstrating that more than a 50% reduction in scan-time can be achieved by Euclidean distance-based matching.
Conclusions: Optimization of the CEST-MRF acquisition schedule is critical for obtaining the best exchange parameter accuracy. The use of Euclidean distance-based matching of signal trajectories simultaneously improved the discrimination ability and reduced the scan time and maximal saturation power required.
Keywords: chemical exchange rate; chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST); magnetic resonance fingerprinting (MRF); optimization; pH; quantitative imaging.
© 2019 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures





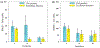
References
-
- Ward KM, Balaban RS. Determination of pH using water protons and chemical exchange dependent saturation transfer (CEST). Magn Reson Med. 2000;44:799–802. - PubMed
-
- Zaiss M, Bachert P. Chemical exchange saturation transfer (CEST) and MR Z-spectroscopy in vivo: a review of theoretical approaches and methods. Phys Med Biol. 2013;58:R221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

