Association between normal triglyceride and insulin resistance in US adults without other risk factors: a cross-sectional study from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007-2014
- PMID: 31401596
- PMCID: PMC6701626
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-028652
Association between normal triglyceride and insulin resistance in US adults without other risk factors: a cross-sectional study from the US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007-2014
Abstract
Objective: Traditionally, the absence of insulin resistance risk factors (IRRFs) was considered a low risk for insulin resistance (IR). However, IR also existed in certain individuals without IRRFs; thus this study aims to explore predictors of IR targeted at the population without IRRFs.
Design: Cross-sectional survey.
Setting: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
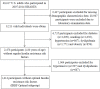
Participants: Participants without regular IRRFs (IRRF-Free, n=2478) and a subgroup without optimal IRRFs (IRRF-Optimal, n=1414) were involved in this study.
Primary and secondary outcome measure: IRRFs and the optimal cut-off value of triglyceride (TG) to predict IR.
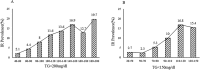
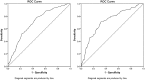
Results: Overall, the prevalence of IR was 6.9% and 5.7% in the IRRF-Free group and the IRRF-Optimal group, respectively. TG and waist circumference were independently associated with the prevalence of IR in both the groups (OR=1.010 to 10.20; p<0.05 for all), where TG was positively associated with IR. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of TG was 0.7016 (95% CI: 0.7013 to 0.7018) and 0.7219 (95% CI: 0.7215 to 0.7222), and the optimal cut-off value of TG to predict IR was 79.5 mg/dL and 81.5 mg/dL in the IRRF-Free group and the IRRF-Optimal group, respectively.
Conclusion: There is an association between TG and IR even in the normal range of TG concentration. Therefore, normal TG could be used as an important indicator to predict the prevalence of IR in the absence of IRRFs.
Keywords: NHANES; ROC curve; insulin resistance; risk factors; triglyceride.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
