Chemical Induction of Aminoglycoside Uptake Overcomes Antibiotic Tolerance and Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 31402316
- PMCID: PMC6800641
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.07.009
Chemical Induction of Aminoglycoside Uptake Overcomes Antibiotic Tolerance and Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
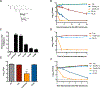
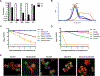
Aminoglycoside antibiotics require proton motive force (PMF) for bacterial internalization. In non-respiring populations, PMF drops below the level required for drug influx, limiting the utility of aminoglycosides against strict and facultative anaerobes. We recently demonstrated that rhamnolipids (RLs), biosurfactant molecules produced by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, potentiate aminoglycoside activity against Staphylococcus aureus. Here, we demonstrate that RLs induce PMF-independent aminoglycoside uptake to restore sensitivity to otherwise tolerant persister, biofilm, small colony variant, and anaerobic populations of S. aureus. Furthermore, we show that this approach represses the rise of resistance, restores sensitivity to highly resistant clinical isolates, and is effective against other Gram-positive pathogens. Finally, while other membrane-acting agents can synergize with aminoglycosides, induction of PMF-independent uptake is uncommon, and distinct to RLs among several compounds tested. In all, small-molecule induction of PMF-independent aminoglycoside uptake circumvents phenotypic tolerance, overcomes genotypic resistance, and expands the utility of aminoglycosides against intrinsically recalcitrant bacterial populations.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; aminoglycosides; antibiotics; biofilm; persisters; resistance; rhamnolipids; tolerance.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests
LCR, SER and BPC are inventors on a patent describing rhamnolipid potentiation of aminoglycoside killing (Radlinski LC, Conlon SR, Conlon BP, Potentiation of antibiotic effect, US 62/534450 Filed July 19 2017). The other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
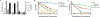
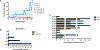
Comment in
-
Membrane-Active Rhamnolipids Overcome Aminoglycoside Resistance.Cell Chem Biol. 2019 Oct 17;26(10):1333-1334. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2019.09.015. Cell Chem Biol. 2019. PMID: 31626780
Similar articles
-
Rapid Freezing Enables Aminoglycosides To Eradicate Bacterial Persisters via Enhancing Mechanosensitive Channel MscL-Mediated Antibiotic Uptake.mBio. 2020 Feb 11;11(1):e03239-19. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03239-19. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32047133 Free PMC article.
-
Host Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Potentiate Aminoglycoside Killing of Staphylococcus aureus.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Apr 27;10(2):e0276721. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.02767-21. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35377191 Free PMC article.
-
Stimulating Aminoglycoside Uptake to Kill Staphylococcus aureus Persisters.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2357:223-236. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1621-5_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34590262
-
Comparison of the next-generation aminoglycoside plazomicin to gentamicin, tobramycin and amikacin.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012 Apr;10(4):459-73. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.25. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012. PMID: 22512755 Review.
-
Development of aminoglycoside antibiotics effective against resistant bacterial strains.Curr Top Med Chem. 2010;10(18):1898-26. doi: 10.2174/156802610793176684. Curr Top Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20615188 Review.
Cited by
-
Gram-negative bacteria act as a reservoir for aminoglycoside antibiotics that interact with host factors to enhance bacterial killing in a mouse model of pneumonia.FEMS Microbes. 2022 May 13;3:xtac016. doi: 10.1093/femsmc/xtac016. eCollection 2022. FEMS Microbes. 2022. PMID: 35909464 Free PMC article.
-
Designer broad-spectrum polyimidazolium antibiotics.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Dec 8;117(49):31376-31385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2011024117. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 33229526 Free PMC article.
-
Controllable self-cleaning FET self-assembled RNA-cleaving DNAzyme based DNA nanotree for culture-free Staphylococcus aureus detection.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Jul 15;22(1):414. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02682-3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39010059 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Efficacy against Antibiotic-Tolerant Staphylococcus aureus Depends on the Mechanism of Antibiotic Tolerance.Antibiotics (Basel). 2022 Dec 13;11(12):1810. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics11121810. Antibiotics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551467 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanosensitive Channels Mediate Hypoionic Shock-Induced Aminoglycoside Potentiation against Bacterial Persisters by Enhancing Antibiotic Uptake.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022 Feb 15;66(2):e0112521. doi: 10.1128/AAC.01125-21. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2022. PMID: 34902270 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

