Noroviruses subvert the core stress granule component G3BP1 to promote viral VPg-dependent translation
- PMID: 31403400
- PMCID: PMC6739877
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.46681
Noroviruses subvert the core stress granule component G3BP1 to promote viral VPg-dependent translation
Abstract
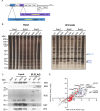
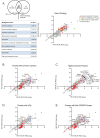
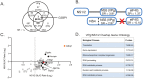
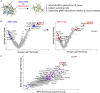
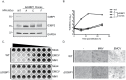
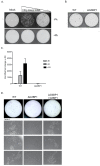
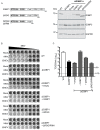
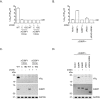
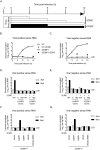
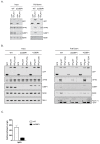
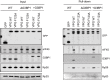
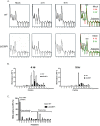
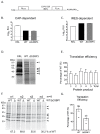
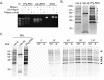
Knowledge of the host factors required for norovirus replication has been hindered by the challenges associated with culturing human noroviruses. We have combined proteomic analysis of the viral translation and replication complexes with a CRISPR screen, to identify host factors required for norovirus infection. The core stress granule component G3BP1 was identified as a host factor essential for efficient human and murine norovirus infection, demonstrating a conserved function across the Norovirus genus. Furthermore, we show that G3BP1 functions in the novel paradigm of viral VPg-dependent translation initiation, contributing to the assembly of translation complexes on the VPg-linked viral positive sense RNA genome by facilitating ribosome recruitment. Our data uncovers a novel function for G3BP1 in the life cycle of positive sense RNA viruses and identifies the first host factor with pan-norovirus pro-viral activity.
Keywords: CRISPR; G3BP1; Norovirus; infectious disease; microbiology; stress granule; translation; virus.
© 2019, Hosmillo et al.
Conflict of interest statement
MH, JL, MM, JE, XW, EE, PD, YC, TF, MT, MP, GM, NL, CW, IG No competing interests declared
Figures


References
-
- Bailey D, Karakasiliotis I, Vashist S, Chung LM, Rees J, Reese J, McFadden N, Benson A, Yarovinsky F, Simmonds P, Goodfellow I. Functional analysis of RNA structures present at the 3' extremity of the murine Norovirus genome: the variable polypyrimidine tract plays a role in viral virulence. Journal of Virology. 2010;84:2859–2870. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02053-09. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

