Hemodialysis-induced changes in hematocrit, hemoglobin and total protein: Implications for relative blood volume monitoring
- PMID: 31404089
- PMCID: PMC6690539
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0220764
Hemodialysis-induced changes in hematocrit, hemoglobin and total protein: Implications for relative blood volume monitoring
Abstract
Background: Relative blood volume (RBV) changes during hemodialysis (HD) are typically estimated based on online measurements of hematocrit, hemoglobin or total blood protein. The aim of this study was to assess changes in the above parameters during HD in order to compare the potential differences in the RBV changes estimated by individual methods.
Methods: 25 anuric maintenance HD patients were monitored during a 1-week conventional HD treatment. Blood samples were collected from the arterial dialysis blood line at the beginning and at the end of each HD session. The analysis of blood samples was performed using the hematology analyzer Advia 2120 and clinical chemistry analyzer Advia 1800 (Siemens Healthcare).
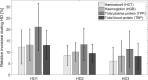
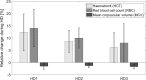
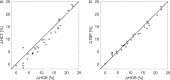
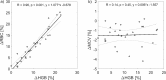
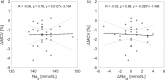
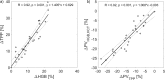
Results: During the analyzed 30 HD sessions with ultrafiltration in the range 0.7-4.0 L (2.5 ± 0.8 L) hematocrit (HCT) increased by 9.1 ± 7.0% (mean ± SD), hemoglobin (HGB) increased by 10.6 ± 6.3%, total plasma protein (TPP) increased by 15.6 ± 9.5%, total blood protein (TBP) increased by 10.4 ± 5.8%, red blood cell count (RBC) increased by 10.8 ± 7.1%, while mean corpuscular red cell volume (MCV) decreased by 1.5 ± 1.1% (all changes statistically significant, p < 0.001). HGB increased on average by 1.5% more than HCT (p < 0.001). The difference between HGB and TBP increase was insignificant (p = 0.16).
Conclusions: Tracking HGB or TBP can be treated as equivalent for the purpose of estimating RBV changes during HD. Due to the reduction of MCV, the HCT-based estimate of RBV changes may underestimate the actual blood volume changes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Polaschegg H., Levin N.: Hemodialysis machines and monitors In Hörl W., Koch K., Lindsay R., Ronco C., Winchester J., eds.: Replacement of Renal Function by Dialysis 5th edn Springer; Netherlands, Dordrecht: (2004)
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

