MAPT p.V363I mutation: A rare cause of corticobasal degeneration
- PMID: 31404212
- PMCID: PMC6659135
- DOI: 10.1212/NXG.0000000000000347
MAPT p.V363I mutation: A rare cause of corticobasal degeneration
Abstract
Objective: Patients with corticobasal syndrome (CBS) present with heterogeneous clinical features, including asymmetric parkinsonism, dyspraxia, aphasia, and cognitive impairment; to better understand the genetic etiology of this rare disease, we undertook a genetic analysis of microtubule-associated protein tau (MAPT).
Methods: We performed a genetic evaluation of MAPT mutations in 826 neurologically healthy controls and 173 cases with CBS using the Illumina NeuroChip genotyping array.
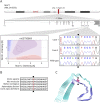
Results: We identified 2 patients with CBS heterozygous for a rare mutation in MAPT (p.V363I) that is located in the highly conserved microtubule-binding domain. One patient was pathologically confirmed and demonstrated extensive 4-repeat-tau-positive thread pathology, achromatic neurons, and astrocytic plaques consistent with corticobasal degeneration (CBD).
Conclusions: We report 2 CBS cases carrying the rare p.V363I MAPT mutation, one of which was pathologically confirmed as CBD. Our findings support the notion that this rare coding change is pathogenic.
Figures

References
-
- Poorkaj P, Bird TD, Wijsman E, et al. . Tau is a candidate gene for chromosome 17 frontotemporal dementia. Ann Neurol 1998;43:815–825. - PubMed
-
- Hutton M, Lendon CL, Rizzu P, et al. . Association of missense and 5'-splice-site mutations in tau with the inherited dementia FTDP-17. Nature 1998;393:702–705. - PubMed
-
- Pickering-Brown SM, Rollinson S, Du Plessis D, et al. . Frequency and clinical characteristics of progranulin mutation carriers in the Manchester frontotemporal lobar degeneration cohort: comparison with patients with MAPT and no known mutations. Brain 2008;131:721–731. - PubMed
Grants and funding
- P30 AG053760/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- MR/S000992/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- Z01 AG000949/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0900652/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K23 AG059891/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- G0502157/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0400074/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- P50 NS038377/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG019610/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- ZIA NS003154/ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- U24 NS072026/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
