Soft tissue sarcomas of the upper extremities: Maximizing treatment opportunities and outcomes
- PMID: 31404317
- PMCID: PMC6676724
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2019.10575
Soft tissue sarcomas of the upper extremities: Maximizing treatment opportunities and outcomes
Abstract
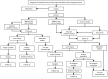
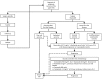
Soft tissue sarcomas (STS) are rare tumors; they do not even equate to 1% of all malignant tumor cases. One-fifth of all STS occur in the upper extremities, where epithelioid sarcoma, synovial sarcoma, clear cell sarcoma and malignant fibrohistiocytoma are the most frequent subtypes. Surgical resection is the cornerstone of treatment. However, accomplishment of optimal oncological and functional results of STS of the upper extremities may represent a challenge for hand surgeons, due to the complex anatomy. In several cases, preoperative therapies are needed to facilitate tumor resection and improve the oncological outcome. Oligometastatic disease may also be a challenging scenario as curative strategies can be applied. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy are commonly used for this purpose albeit with conflicting evidence. Novel drug combinations have also been approved in the metastatic setting, further improving the quality of life and survival of eligible patients. Thus, prior to any approach, every case should be individually discussed in sarcoma centers with specialized multidisciplinary tumor boards. The aim of the present review was to gather the multidisciplinary experiences of the available therapeutic strategies for STS of the upper extremities.
Keywords: adjuvant therapy; chemotherapy; hand; limb sparing surgery; metastases; radiotherapy; soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
