The Synthesis, Structure, Morphology Characterizations and Evolution Mechanisms of Nanosized Titanium Carbides and Their Further Applications
- PMID: 31405228
- PMCID: PMC6723659
- DOI: 10.3390/nano9081152
The Synthesis, Structure, Morphology Characterizations and Evolution Mechanisms of Nanosized Titanium Carbides and Their Further Applications
Abstract
It is widely known that the special performances and extensive applications of the nanoscale materials are determined by their as-synthesized structures, especially their growth sizes and morphologies. Hereinto, titanium carbides, which show brilliant comprehensive properties, have attracted considerable attention from researchers. How to give full play to their potentials in the light-weight manufacture, microwave absorption, electromagnetic protection, energy conversion and catalyst areas has been widely studied. In this summarized article, the synthesis methods and mechanisms, corresponding growth morphologies of titanium carbides and their further applications were briefly reviewed and analyzed according to their different morphological dimensions, including one-dimensional nanostructures, two-dimensional nanosheets and three-dimensional nanoparticles. It is believed that through the investigation of the crystal structures, synthesis methods, growth mechanisms, and morphology characterizations of those titanium carbides, new lights could be shed on the regulation and control of the ceramic phase specific morphologies to meet with their excellent properties and applications. In addition, the corresponding development prospects and challenges of titanium carbides with various growth morphologies were also summarized.
Keywords: crystal growth mechanism; excellent performances; morphology evolution manipulation; nanostructures; titanium carbides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures





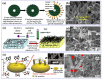




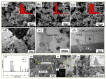
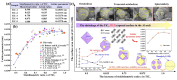

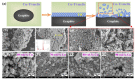

References
-
- Yang H.B., Gao T., Wu Y.Y., Zhang H.N., Nie J.J., Liu X.F. Microstructure and mechanical properties at both room and high temperature of in-situ TiC reinforced Al-4.5Cu matrix nanocomposite. J. Alloys Compd. 2018;767:606–616. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.07.045. - DOI
-
- Dai B.Z., Zhao B., Xie X., Su T.T., Fan B.B., Zhang R., Yang R. Novel two-dimensional Ti3C2Tx MXenes/nano-carbon sphere hybrids for high-performance microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2018;6:5690–5697. doi: 10.1039/C8TC01404C. - DOI
-
- Liu Y., Jian X.Y., Su X.L., Luo F., Xu J., Wang J.B. Electromagnetic interference shielding and absorption properties of Ti3SiC2/nano Cu/epoxy resin coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2018;740:68–76. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.017. - DOI
-
- Fan D., Lu S.H., Guo Y.D., Hu X.J. Two-dimensional tetragonal titanium carbide: A high-capacity and high-rate battery material. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2018;122:15118–15124. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b03425. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

