Metformin as Anti-Aging Therapy: Is It for Everyone?
- PMID: 31405774
- PMCID: PMC6779524
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tem.2019.07.015
Metformin as Anti-Aging Therapy: Is It for Everyone?
Abstract
Metformin is the most widely prescribed oral hypoglycemic medication for type 2 diabetes worldwide. Metformin also retards aging in model organisms and reduces the incidence of aging-related diseases such as neurodegenerative disease and cancer in humans. In spite of its widespread use, the mechanisms by which metformin exerts favorable effects on aging remain largely unknown. Further, not all individuals prescribed metformin derive the same benefit and some develop side effects. Before metformin finds its way to mainstay therapy for anti-aging, a more granular understanding of the effects of the drug in humans is needed. This review provides an overview of recent findings from metformin studies in aging and longevity and discusses the use of metformin to combat aging and aging-related diseases.
Keywords: aging; lysosome; metformin; mitochondria; personalized medicine; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
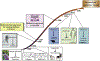
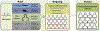
References
-
- Bailey CJ (2017) Metformin: historical overview. Diabetologia 60 (9), 1566–1576. - PubMed
-
- Werner A and Bell J (1922) The preparation of methylguanidine, and of ββ-dimethylguanidine by the interaction of dicyandiamide, and methylammonium and dimethylammonium chlorides respectively. Journal of the Chemical Society, Transactions 121, 1790–1794.
-
- Inzucchi SE et al. (2015) Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 38 (1), 140–9. - PubMed
-
- Abu Hashim H (2016) Twenty years of ovulation induction with metformin for PCOS; what is the best available evidence? Reprod Biomed Online 32 (1), 44–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

