Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome
- PMID: 31406327
- PMCID: PMC6776680
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-019-0217-9
Accurate circular consensus long-read sequencing improves variant detection and assembly of a human genome
Abstract
The DNA sequencing technologies in use today produce either highly accurate short reads or less-accurate long reads. We report the optimization of circular consensus sequencing (CCS) to improve the accuracy of single-molecule real-time (SMRT) sequencing (PacBio) and generate highly accurate (99.8%) long high-fidelity (HiFi) reads with an average length of 13.5 kilobases (kb). We applied our approach to sequence the well-characterized human HG002/NA24385 genome and obtained precision and recall rates of at least 99.91% for single-nucleotide variants (SNVs), 95.98% for insertions and deletions <50 bp (indels) and 95.99% for structural variants. Our CCS method matches or exceeds the ability of short-read sequencing to detect small variants and structural variants. We estimate that 2,434 discordances are correctable mistakes in the 'genome in a bottle' (GIAB) benchmark set. Nearly all (99.64%) variants can be phased into haplotypes, further improving variant detection. De novo genome assembly using CCS reads alone produced a contiguous and accurate genome with a contig N50 of >15 megabases (Mb) and concordance of 99.997%, substantially outperforming assembly with less-accurate long reads.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Financial Interests Statement
A.M.W., A.T., D.R.R., G.T.C., M.W.H., P.P., R.J.H., W.J.R., and Y.Q. are employees and shareholders of Pacific Biosciences. A.C., A.K., M.A.D., and P.C. are employees and shareholders of Google. A.F. and C-S.C. are employees and shareholders of DNAnexus. A.C. is a shareholder and was an employee of DNAnexus for a portion of this work.
Figures


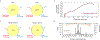
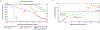
References
-
- DNA Sequencing Costs: Data. National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) Available at: https://www.genome.gov/27541954/dna-sequencing-costs-data/. (Accessed: 7th December 2018)
-
- Smith LM et al. Fluorescence detection in automated DNA sequence analysis. Nature 321, 674–679 (1986). - PubMed
-
- Lander ES et al. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409, 860–921 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Venter JC et al. The sequence of the human genome. Science 291, 1304–1351 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

