An Nfil3-Zeb2-Id2 pathway imposes Irf8 enhancer switching during cDC1 development
- PMID: 31406377
- PMCID: PMC6707889
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-019-0449-3
An Nfil3-Zeb2-Id2 pathway imposes Irf8 enhancer switching during cDC1 development
Abstract
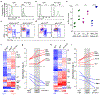
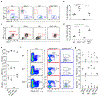
Classical type 1 dendritic cells (cDC1s) are required for antiviral and antitumor immunity, which necessitates an understanding of their development. Development of the cDC1 progenitor requires an E-protein-dependent enhancer located 41 kilobases downstream of the transcription start site of the transcription factor Irf8 (+41-kb Irf8 enhancer), but its maturation instead requires the Batf3-dependent +32-kb Irf8 enhancer. To understand this switch, we performed single-cell RNA sequencing of the common dendritic cell progenitor (CDP) and identified a cluster of cells that expressed transcription factors that influence cDC1 development, such as Nfil3, Id2 and Zeb2. Genetic epistasis among these factors revealed that Nfil3 expression is required for the transition from Zeb2hi and Id2lo CDPs to Zeb2lo and Id2hi CDPs, which represent the earliest committed cDC1 progenitors. This genetic circuit blocks E-protein activity to exclude plasmacytoid dendritic cell potential and explains the switch in Irf8 enhancer usage during cDC1 development.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Cella M et al., Plasmacytoid monocytes migrate to inflamed lymph nodes and produce large amounts of type I interferon [see comments]. Nature Medicine 5, 919–923 (1999). - PubMed
-
- Naik SH et al., Development of plasmacytoid and conventional dendritic cell subtypes from single precursor cells derived in vitro and in vivo. Nat Immunol 8, 1217–1226 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- RM1 HG007735/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI150297/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HG007735/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- K08 CA230188/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA248919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI076427/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR073752/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI162643/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F30 DK108498/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

