The impact of the patient's condition, diagnostic procedures and treatment on the survival of carcinoma of unknown primary site patients
- PMID: 31406475
- PMCID: PMC6642654
- DOI: 10.2147/CMAR.S204346
The impact of the patient's condition, diagnostic procedures and treatment on the survival of carcinoma of unknown primary site patients
Abstract
Introduction: Carcinoma of unknown primary site (CUP) refers to 1-5% of all head and neck neoplasms. Very often, the primary site remains difficult to determine. Squamous cell carcinoma is the most frequent histopathological type diagnosed in the head and neck region. According to statistics, a primary site is usually located in the oropharynx.
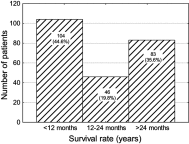
Study objective: The study presents diagnostic difficulties and the methods of diagnosing and the therapy of CUP and primary sites in patients treated in the region of Lower Silesia and Silesia. The aim of the study was to show a retrospective analysis of 233 CUP patients to assess how clinical features, diagnosis and treatment affect the survival of patients.
Material and methods: The diagnostics of patients included panendoscopy with specimen collection (nasoendoscopy, laryngoscopy, esophagoscopy, brochoscopy), computed tomography examination of the neck, chest, abdomen and pelvis minor, as well as positron emission tomography examination. Tonsilletomy was performed in 37 patients. Neck dissection was carried out in 109 subjects and 165 patients were treated bt radiotherapy, and 135 by chemotherapy.
Conclusions: Tonsillectomy is required in CUP patients with the negative results of biopsy and imaging tests. It gives a possibility of detecting the primary site and improves the results of treatment and survival of CUP patients.Combination therapy, including surgical treatment and chemoradiotherapy, gives the best therapeutic results in CUP patients. The general condition of patient and younger age have an impact on prognosis and survival.
Keywords: carcinoma of unknown primary site; head and neck cancer; head and neck surgery; squamous cell carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Nabili V, Zaia B, Blackwell KE, Head CS, Grabski K, Sercarz JA. Position emission tomography: poor sensitivity for occult tonsillar cancer. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg. 2007;28:153–157. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources