Analysis of NF-κB Pathway Proteins in Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma: Correlations with EBV Status and Clinical Outcome-A Children's Oncology Group Study
- PMID: 31406604
- PMCID: PMC6690044
- DOI: 10.1155/2012/341629
Analysis of NF-κB Pathway Proteins in Pediatric Hodgkin Lymphoma: Correlations with EBV Status and Clinical Outcome-A Children's Oncology Group Study
Abstract
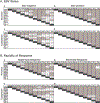
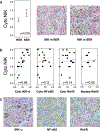
Constitutively active nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) is integral to the survival of Hodgkin/Reed-Sternberg cells (H/RS) in Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL). To investigate NF-κB pathway proteins in pediatric HL, we utilized a tissue microarray compiled from 102 children enrolled in the Children's Oncology Group intermediate-risk clinical trial AHOD0031 (56 male, 78 Caucasian, median age 15y (range 1-20y), 85 nodular sclerosing subtype, 23 Epstein Barr virus (EBV) positive, 24 refractory/relapsed disease). We examined the intensity, localization, and pathway correlations of NF-κB pathway proteins (Rel-A/p65, Rel-B, c-Rel, NF-κB1, NF-κB2, IκB-α, IKK-α, IKK-β, IKK-γ/NEMO, NIK, A20), as well as their associations with EBV status and clinical outcome. NF-κB pathway proteins were overexpressed in pediatric HL patients compared to controls. Patients with EBV-tumors, or with rapid early therapy response, had tightly coordinated regulation of NF-κB pathway proteins, whereas patients with EBV+ tumors, or slow early therapy response, had little coordinated NF-κB pathway regulation. High NIK expression was associated with a slow response to therapy and decreased EFS. Elevated Rel-B, NIK and the NF-κB inhibitor A20 were associated with decreased EFS in multivariate analysis. These studies suggest a pivotal role for the NF-κB pathway in therapy response and patient survival (clinicaltrials.gov identifier: ).
Keywords: ABVD; AHOD0031; Epstein-Barr virus; Hodgkin Disease; NF-kappaB.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES The authors report no potential conflicts of interest and no competing interests.
Figures



References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
