[Efficacy and safety of a loading high-dose tranexamic acid followed by postoperative five doses in total hip arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial]
- PMID: 31407549
- PMCID: PMC8337895
- DOI: 10.7507/1002-1892.201902075
[Efficacy and safety of a loading high-dose tranexamic acid followed by postoperative five doses in total hip arthroplasty: A randomized controlled trial]
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy and safety of a loading high-dose tranexamic acid (TXA) followed by postoperative 5 doses in total hip arthroplasty (THA) by a randomized controlled trial.
Methods: Seventy-two patients who underwent primary unilateral THA between December 2017 and March 2018 were randomly divided into two groups (36 patients in each group). A single dose of 20 mg/kg TXA was administered intravenously before 5-10 minutes of operation in group A; and a single dose of 40 mg/kg TXA was administered intravenously in group B at the same time point. All patients received 5 doses of 1 g TXA at 3, 6, 12, 18, and 24 hours after the first dose. There was no significant difference in gender, age, weight, height, body mass index, disease type, and combined medical diseases between the two groups ( P>0.05). Total blood loss (TBL), lowest postoperative hemoglobin (Hb) level, fibrinolysis parameters [fibrin (ogen) degradation products (FDP), D-dimer], inflammatory factors [C-reaction protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6)], adverse events (thrombosis, pulmonary embolism) were recorded and compared between groups.
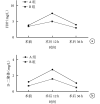
Results: The TBL was significantly lower in group B than in group A ( P<0.05). Furthermore, the lowest postoperative Hb level was significantly higher in group B than in group A ( P<0.05). There was no significant difference in FDP and D-dimer before operation between the two groups ( P>0.05). The levels of FDP and D-dimer were significantly lower in group B than in group A at 12 and 36 hours postoperatively ( P<0.05). There was no significant difference in CRP and IL-6 before operation between the two groups ( P>0.05). The levels of CRP and IL-6 were significant lower in group B than in group A at 12, 24, and 36 hours postoperatively ( P<0.05). There was no significant difference at 14 days ( P>0.05). There were 2 patients with intramuscular venous thrombosis in group A and 1 in group B after operation, and there was no significant difference in the incidence of embolic events ( P>0.05). No deep venous thrombosis or pulmonary embolism occurred in all groups.
Conclusion: A loading high-dose TXA followed by postoperative 5 doses can further reduce the blood loss, provide additional fibrinolysis and inflammation control in THA, without increasing the risk of embolic events.
目的: 通过前瞻性临床对比研究,探讨人工全髋关节置换术(total hip arthroplasty,THA)中首次大剂量联合术后 5 次静脉应用氨甲环酸(tranexamic acid,TXA)的有效性及安全性。.
方法: 以 2017 年 12 月—2018 年 3 月拟初次行单侧 THA 且符合选择标准的 72 例患者纳入研究,随机分为 A、B 两组( n=36)。THA 术前 5~10 min A、B 组分别按照 20、40 mg/kg 静脉滴注 TXA;两组首次使用后 3、6、12、18、24 h 分别静脉滴注 1 g TXA。两组患者性别、年龄、体质量、身高、体质量指数、疾病类型以及术前合并症等一般资料比较,差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05)。记录并比较两组围术期总失血量以及术后 3 d 内血红蛋白最低值;术前及术后 12、36 h 测量纤溶指标纤维蛋白(原)降解产物[fibrin(ogen)degradation products,FDP]及 D-二聚体水平,术前以及术后 12、24、36 h 及 14 d 测量炎性指标 C 反应蛋白(C-reaction protein,CRP)及 IL-6 水平。观察有无血栓形成以及肺栓塞发生。.
结果: B 组围术期总失血量明显低于 A 组,术后血红蛋白最低值明显高于 A 组,差异均有统计学意义( P<0.05)。术前两组 FDP 及 D-二聚体水平差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05),B 组术后 12、36 h 上述指标均低于 A 组( P<0.05)。术前两组 CRP 及 IL-6 差异均无统计学意义( P>0.05);术后 12、24、36 h B 组 CRP 及 IL-6 水平均低于 A 组( P<0.05),14 d 两组差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。A 组 2 例、B 组 1 例术后发生肌间静脉血栓,两组差异无统计学意义( P>0.05)。两组均无输血、下肢深静脉血栓形成、肺栓塞事件发生。.
结论: 首次大剂量联合术后 5 次静脉应用 TXA 可以进一步减少 THA 围术期失血,抑制纤溶,降低术后炎性反应,而且不增加血栓并发症风险。.
Keywords: Tranexamic acid; blood loss; perioperative period; total hip arthroplasty.
Conflict of interest statement
利益冲突:所有作者声明,在课题研究和文章撰写过程中不存在利益冲突。
Figures
References
-
- Xie J, Hu Q, Ma J, et al Multiple boluses of intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce hidden blood loss and the inflammatory response following enhanced-recovery primary total hip arthroplasty: a randomised clinical trial. Bone Joint J. 2017;99-B(11):1442–1449. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.99B11.BJJ-2017-0488.R1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- 龙也, 王通, 刘佳鑫, 等 重组人促红细胞生成素联合铁剂纠正老年股骨转子间骨折患者围术期贫血的临床研究. 中国修复重建外科杂志. 2019;33(6):662–665.
-
- 李锐博, 尹诗九, 钟航, 等 静脉联合关节腔内注射氨甲环酸后引流管夹闭时间对人工全膝关节置换术后失血量的影响及安全性评价. 中国修复重建外科杂志. 2017;31(4):417–421.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous