Effect of Pushen capsule for treating vascular mild cognitive impairment: a pilot observational study
- PMID: 31407622
- PMCID: PMC6862923
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060519859766
Effect of Pushen capsule for treating vascular mild cognitive impairment: a pilot observational study
Abstract
Objective: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) may be beneficial for vascular dementia (VaD). We evaluated the efficacy of Pushen capsule, a compound containing several TCM components, for treating vascular mild cognitive impairment (VaMCI).
Methods: Seventy outpatients with VaMCI were randomized to Pushen capsule or control treatment with Ginkgo biloba. Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), and Subjective Memory Loss Rating Scale scores; and lipid, lipoprotein, and haemorheological parameters were collected at baseline, week 4, and week 12 of treatment.
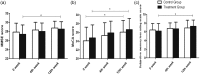
Results: MMSE score at week 12 was significantly higher in the treatment group compared with baseline (t = −2.352) but was not significantly different from week 12 in the control group. The MoCA score at week 12 was higher than that at baseline for both the treatment and control groups (t = −2.619 and −2.582, respectively), as was the “delayed recall” item score. Subjective memory loss score and the cognitive function “forgetting acquaintance's name” were significantly higher in the treatment group at week 12 than at baseline (t = −2.621 and χ2 = 4.419, respectively). Lipid, lipoprotein, and haemorheological parameters were significantly different after treatment in both groups.
Conclusion: The benefits of Pushen capsule on cognitive function in VaMCI were comparable with that of Ginkgo biloba.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba; Mini Mental State Examination; Pushen capsule; Vascular mild cognitive impairment; cognitive function; randomized controlled trial.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of Memo®, a natural formula combination, on Mini-Mental State Examination scores in patients with mild cognitive impairment.Clin Interv Aging. 2013;8:975-81. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S44777. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Clin Interv Aging. 2013. PMID: 23950642 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in improving episodic memory of patients with mild cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial].Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012 Jun;10(6):628-34. doi: 10.3736/jcim20120605. Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Xue Bao. 2012. PMID: 22704410 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
[Effects of ginkgo biloba tablet in treating mild cognitive impairment].Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012 Sep;32(9):1208-11. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23185760 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Neurovascular glial unit: A target of phytotherapy for cognitive impairments.Phytomedicine. 2023 Oct;119:155009. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155009. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37573807
-
Chinese Herbal Medicine for Mild Cognitive Impairment Using Montreal Cognitive Assessment: A Systematic Review.J Altern Complement Med. 2019 Jun;25(6):578-592. doi: 10.1089/acm.2018.0346. Epub 2019 Mar 28. J Altern Complement Med. 2019. PMID: 30920303
Cited by
-
Evidence-based evaluation of adjuvant therapy with Chinese medicine for cerebral small vessel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Dec 29;102(52):e36221. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000036221. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 38206688 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of ginkgo preparation in patients with vascular dementia: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 11;99(37):e22209. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022209. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32925798 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Polyphenols on Working and Episodic Memory in Non-pathological and Pathological Aging: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Nutr. 2022 Jan 26;8:720756. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.720756. eCollection 2021. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35155509 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of twenty-one nutrients and phytonutrients on cognitive function: A narrative review.J Clin Transl Res. 2021 Aug 4;7(4):575-620. eCollection 2021 Aug 26. J Clin Transl Res. 2021. PMID: 34541370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Buyang Huanwu Decoction for the Treatment of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jun 29;16:942188. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.942188. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35844225 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Dementia – Fact Sheet Detail. World Health Organization, 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia. [Last accessed on 2019 May 14].
-
- Chan KY, Wang W, Wu JJ, et al. Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia in China, 1990-2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013; 381: 2016–2023. - PubMed
-
- Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8: 1006–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical