Effect of Pushen capsule for treating vascular mild cognitive impairment: a pilot observational study
- PMID: 31407622
- PMCID: PMC6862923
- DOI: 10.1177/0300060519859766
Effect of Pushen capsule for treating vascular mild cognitive impairment: a pilot observational study
Abstract
Objective: Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) may be beneficial for vascular dementia (VaD). We evaluated the efficacy of Pushen capsule, a compound containing several TCM components, for treating vascular mild cognitive impairment (VaMCI).
Methods: Seventy outpatients with VaMCI were randomized to Pushen capsule or control treatment with Ginkgo biloba. Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE), Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA), and Subjective Memory Loss Rating Scale scores; and lipid, lipoprotein, and haemorheological parameters were collected at baseline, week 4, and week 12 of treatment.
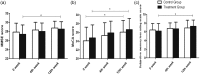
Results: MMSE score at week 12 was significantly higher in the treatment group compared with baseline (t = −2.352) but was not significantly different from week 12 in the control group. The MoCA score at week 12 was higher than that at baseline for both the treatment and control groups (t = −2.619 and −2.582, respectively), as was the “delayed recall” item score. Subjective memory loss score and the cognitive function “forgetting acquaintance's name” were significantly higher in the treatment group at week 12 than at baseline (t = −2.621 and χ2 = 4.419, respectively). Lipid, lipoprotein, and haemorheological parameters were significantly different after treatment in both groups.
Conclusion: The benefits of Pushen capsule on cognitive function in VaMCI were comparable with that of Ginkgo biloba.
Keywords: Ginkgo biloba; Mini Mental State Examination; Pushen capsule; Vascular mild cognitive impairment; cognitive function; randomized controlled trial.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Dementia – Fact Sheet Detail. World Health Organization, 2019. Available from: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia. [Last accessed on 2019 May 14].
-
- Chan KY, Wang W, Wu JJ, et al. Epidemiology of Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia in China, 1990-2010: a systematic review and analysis. Lancet 2013; 381: 2016–2023. - PubMed
-
- Pendlebury ST, Rothwell PM. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol 2009; 8: 1006–1018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical