Association between Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Aggressiveness in Thyroid Cancer
- PMID: 31408968
- PMCID: PMC6721537
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers11081154
Association between Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and Aggressiveness in Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
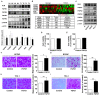
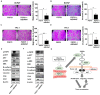
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) plays important roles in regulating glucose, lipid, and energy metabolism; however, its effects in tumors remain poorly understood. To understand the role of FGF21 in regulating tumor aggressiveness in thyroid cancer, serum levels of FGF21 were measured in healthy subjects and patients with papillary thyroid cancer (PTC), and expression levels of FGF21, FGF receptors (FGFRs), and β-klotho (KLB) were investigated in human thyroid tissues. The cell viability, migrating cells, and invading cells were measured in PTC cells after treatment with recombinant FGF21. Higher serum levels of FGF21 were found in patients with thyroid cancer than in control participants, and were significantly associated with body mass index (BMI), fasting glucose levels, triglyceride levels, tumor stage, lymphovascular invasion, and recurrence. Serum FGF21 levels were positively correlated with the BMI in patients with PTC, and significantly associated with recurrence. Recombinant FGF21 led to tumor aggressiveness via activation of the FGFR signaling axis and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) signaling in PTC cells, and AZD4547, an FGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor, attenuated the effects of FGF21. Hence, FGF21 may be a new biomarker for predicting tumor progression, and targeting FGFR may be a novel therapy for the treatment of obese patients with PTC.
Keywords: FGF21; FGFR; cell proliferation; metastasis; obesity; thyroid cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fasting decreases plasma FGF21 in obese subjects and the expression of FGF21 receptors in adipose tissue in both lean and obese subjects.J Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 1;239(1):73–80. doi: 10.1530/JOE-18-0002. J Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 30307155
-
Nutritional regulation of fibroblast growth factor 21: from macronutrients to bioactive dietary compounds.Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016 Sep 1;30(1):/j/hmbci.2017.30.issue-1/hmbci-2016-0034/hmbci-2016-0034.xml. doi: 10.1515/hmbci-2016-0034. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016. PMID: 27583468 Review.
-
Effects of fibroblast growth factor 21 serum level on clinicopathological findings in papillary thyroid carcinoma.Caspian J Intern Med. 2024 Oct 19;16(1):58-65. doi: 10.22088/cjim.16.1.58. eCollection 2025 Winter. Caspian J Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 39619743 Free PMC article.
-
FGFR inhibitors: Effects on cancer cells, tumor microenvironment and whole-body homeostasis (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2016 Jul;38(1):3-15. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2620. Epub 2016 May 31. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27245147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between insulin resistance and impairment of FGF21 signal transduction in skeletal muscles.Endocrine. 2016 Jul;53(1):97-106. doi: 10.1007/s12020-015-0845-x. Epub 2016 Jan 12. Endocrine. 2016. PMID: 26758997
Cited by
-
Low Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Level and Its Altered Regulation by Thyroid Hormones in Patients with Hashimoto's Thyroiditis on Levothyroxine Substitution.Metabolites. 2024 Oct 21;14(10):565. doi: 10.3390/metabo14100565. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 39452947 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatic miR-149-5p upregulation fosters steatosis, inflammation and fibrosis development in mice and in human liver organoids.JHEP Rep. 2024 Jun 4;6(9):101126. doi: 10.1016/j.jhepr.2024.101126. eCollection 2024 Sep. JHEP Rep. 2024. PMID: 39263327 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction Model of Pathologic Central Lymph Node Negativity in cN0 Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 27;11:727984. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.727984. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34646771 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the mitochondrial stress response in human cancer progression.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 May;245(10):861-878. doi: 10.1177/1535370220920558. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 32326760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between Thyroid Carcinoma and Tumor-Correlated Immune Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 22;15(10):2863. doi: 10.3390/cancers15102863. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37345200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dieci M.V., Arnedos M., Andre F., Soria J.C. Fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors as a cancer treatment: From a biologic rationale to medical perspectives. Cancer Discov. 2013;3:264–279. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0362. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Zhang X., Ibrahimi O.A., Olsen S.K., Umemori H., Mohammadi M., Ornitz D.M. Receptor specificity of the fibroblast growth factor family, part II. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;271:15292–15297.
-
- Acevedo V.D., Gangula R.D., Freeman K.W., Li R., Zhang Y., Wang F., Ayala G.E., Peterson L.E., Ittmann M., Spencer D.M. Inducible FGFR-1 activation leads to irreversible prostate adenocarcinoma and an epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell. 2007;12:559–571. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2007.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

