Effect of a dentifrice containing different particle sizes of hydroxyapatite on dentin tubule occlusion and aqueous Cr (VI) sorption
- PMID: 31409987
- PMCID: PMC6643156
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S205804
Effect of a dentifrice containing different particle sizes of hydroxyapatite on dentin tubule occlusion and aqueous Cr (VI) sorption
Abstract
Background: Dentin hypersensitivity is a common negative oral condition that can be treated with dentifrice containing hydroxyapatite (HA). The study evaluated the effect of nano-HA dentifrice on plugging the dentinal tubules for an anti-sensitivity reaction compared to a dentifrice containing common-sized particles. Also, the adsorption capacity of different particle sizes of HA mixed in a dentifrice and which is the optimal particle size was considered.
Methods: Fourty premolar dentine discs and fourty molar dentine discs were randomly divided into 4 groups: distilled water group, ordinary dentifrice group and 80, 300 nm HA dentifrice group. Each dentin disc was brushed with a dentifrice twice daily at 7600 rpm under 100 g force for 2 mins for 7 consecutive days and divided into two parts, half of the dentin disc was detected by the scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS), the other half was brushed with distilled water and observed by SEM. One milliliter dentifrice solution (80 nm HA dentifrice, 300 nm HA dentifrice, ordinary dentifrice) was added to 50 ml potassium dichromate solution for 1, 14, and 28 d. The residual Chromium (Cr6+) concentration in the supernatant was measured by the diphenylcarbon phthalocyanine hydrazine method. The elemental constitution in the precipitate was detected by EDS. The Kruskal-Wallis test was used to analyze surface mineralization and different plugging rates of dentinal tubules. The absorption capacity of dentifrices were also evaluated by the Kruskal-Wallis test.
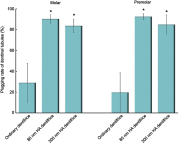
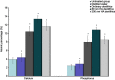
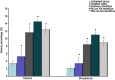
Results: The plugging rate in the HA dentifrice group was higher than that in the ordinary dentifrice group, and the 80 nm HA dentifrice group showed the best result. The atomic percentages of Ca and P of 80 nm dentifrice group on the surface of dentinal tubules were the highest. The 80 nm HA dentifrice group showed the best adsorption and stable effect of Cr6+, followed by the 300 nm HA dentifrice group. The 300 nm HA dentifrice and the ordinary dentifrice showed desorption phenomenon.
Conclusions: The dentifrice containing HA, especially the 80 nm HA dentifrice, exerts good dentinal tubule occlusion and surface mineralization effect. This dentifrice was also a good adsorbent of Cr6+.
Keywords: chromium ion; dentifrice; dentin hypersensitivity; heavy metal ion; nano-hydroxyapatite.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Effects of dentifrice containing hydroxyapatite on dentinal tubule occlusion and aqueous hexavalent chromium cations sorption: a preliminary study.PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e45283. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0045283. Epub 2012 Dec 28. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23300511 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro dentin tubule occlusion by an arginine-containing dentifrice.Am J Dent. 2019 Jun;32(3):133-137. Am J Dent. 2019. PMID: 31295394
-
[Effect of nanohydroxyapatite on surface mineralization in acid-etched dentinal tubules and adsorption of lead ions].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020 Sep 30;40(9):1307-1312. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2020.09.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2020. PMID: 32990241 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Assessment of the Effectiveness of Desensitizing Dentifrices on Management of Dental Hypersensitivity: An In Vitro Study.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024 May 1;25(5):494-497. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3667. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2024. PMID: 39364850
-
[Impact of particle size and morphology on zinc cation adsorption by hydroxyapatite and dentifrice containing hydroxyapatite].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016 May;36(5):724-8. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2016. PMID: 27222194 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Nanotechnology in toothpaste: Fundamentals, trends, and safety.Heliyon. 2024 Jan 20;10(3):e24949. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e24949. eCollection 2024 Feb 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38317872 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Demineralization Inhibition Effects of Dentin Desensitizers Using Swept-Source Optical Coherence Tomography.Materials (Basel). 2021 Apr 9;14(8):1876. doi: 10.3390/ma14081876. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918865 Free PMC article.
-
Calcium Phosphate Delivery Systems for Regeneration and Biomineralization of Mineralized Tissues of the Craniofacial Complex.Mol Pharm. 2023 Feb 6;20(2):810-828. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.2c00652. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Mol Pharm. 2023. PMID: 36652561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The use of hydroxyapatite toothpaste to prevent dental caries.Odontology. 2022 Apr;110(2):223-230. doi: 10.1007/s10266-021-00675-4. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Odontology. 2022. PMID: 34807345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Effect of Toothpastes Containing Hydroxyapatite, Fluoroapatite, and Zn-Mg-hydroxyapatite Nanocrystals on Dentin Hypersensitivity: A Randomized Clinical Trial.J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2022 Apr 8;12(2):252-259. doi: 10.4103/jispcd.JISPCD_333_21. eCollection 2022 Mar-Apr. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2022. PMID: 35462739 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Addy M. Etiology and clinical implication of dentin hypersensitivity. Dent Clinic North Am. 1990;34:503–514. - PubMed
-
- Addy M. Dentine hypersensitivity: new perspectives on an old problem. Int Dent J. 2002;52:367–375. doi:10.1002/j.1875-595X.2002.tb00936.x - DOI
-
- Canadian Advisory Board on Dentin Hypersensitivity. Consensus-based recommendations for the diagnosis and management of dentin hypersensitivity. J Can Dent Assoc. 2003;69:221–226. - PubMed
-
- Guerra F, Corridore D, Cocco F, et al. Oral health sentinel-based surveillance: a pilot study on dentinal hypersensitivity pain. ClinTer. 2017;168(5):e333–e337. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

