The prognostic value of LINC01296 in pan-cancers and the molecular regulatory mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma: a comprehensive study based on data mining, bioinformatics, and in vitro validation
- PMID: 31410029
- PMCID: PMC6650622
- DOI: 10.2147/OTT.S205853
The prognostic value of LINC01296 in pan-cancers and the molecular regulatory mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma: a comprehensive study based on data mining, bioinformatics, and in vitro validation
Retraction in
-
The Prognostic Value of LINC01296 in Pan-Cancers and the Molecular Regulatory Mechanism in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Study Based on Data Mining, Bioinformatics, and in vitro Validation [Retraction].Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Mar 26;13:2525. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S254588. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32273722 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background and aims: This study aimed to clarify the prognostic role of LINC01296 in various cancers, and to evaluate its effect on proliferation, metastasis, and the cell cycle in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) by data mining, bioinformatics, and in vitro validation.
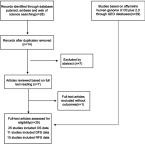
Methods: The prognostic role of LINC01296 in cancer patients was assessed by searching the PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Gene Expression Omnibus databases and calculating pooled hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs); this prognostic role was also evaluated using The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). We detected LINC01296 expression in HCC cell lines, and lentivirus-mediated small interfering RNAs were used to silence LINC01296 in MHCC97H and Hep3B cells to explore the role of LINC01296 in cell proliferation, metastasis, and cell cycle progression with in vitro validation and bioinformatics.
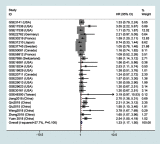
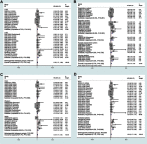
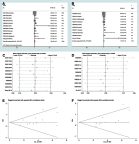
Results: The results indicated that LINC01296 overexpression was associated with poor overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in various cancers; however, LINC01296 expression was not associated with recurrence-free survival (RFS). Similar results were found with TCGA, which showed that LINC01296 expression was associated with the pathologic stage, tumor size, and differentiation in Asian cancer patients. Additionally, bioinformatics analysis revealed expression of 394 related genes, which indicated that LINC01296 could be involved in the tumorigenesis and progression of HCC. In vitro gene silencing experiments indicated that LINC01296 downregulation repressed cell proliferation, cell cycle progression, and the metastatic potential of HCC through the regulation of BUB1, CCNA2, and CDK1 expression.
Conclusion: This study demonstrated that LINC01296 expression is related to poor OS and DFS in a variety of cancer types and that LINC01296 has an oncogenic role in HCC.
Keywords: HCC; LINC01296; bioinformatics; cancers; lncRNA.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Clinicopathological and prognostic value of LINC01296 in cancers: a meta-analysis.Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019 Dec;47(1):3315-3321. doi: 10.1080/21691401.2019.1648284. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31385542
-
LINC01296 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of HCC cells by targeting miR-122-5P and modulating EMT activity.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Mar 26;12:2193-2203. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S197338. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 30988624 Free PMC article.
-
DUXAP8 a Pan-Cancer Prognostic Marker Involved in the Molecular Regulatory Mechanism in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Comprehensive Study Based on Data Mining, Bioinformatics, and in vitro Validation.Onco Targets Ther. 2019 Dec 31;12:11637-11650. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S231750. eCollection 2019. Onco Targets Ther. 2019. PMID: 32021243 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of LINC01296 Expression in Patients with Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020 Aug 1;21(8):2189-2195. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2020.21.8.2189. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2020. PMID: 32856843 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of long non-coding RNA 01296 expression in human solid malignant tumours: a meta-analysis.Postgrad Med J. 2020 Jan;96(1131):43-52. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-136684. Epub 2019 Aug 23. Postgrad Med J. 2020. PMID: 31444240 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of long non-coding RNA LINC01296 in oral squamous cell carcinoma: a study based on bioinformatics analysis and in vitro validation.J Cancer. 2022 Jan 1;13(3):775-783. doi: 10.7150/jca.60417. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35154446 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring molecular and modular insights into space ionizing radiation effects through heterogeneous gene regulatory networks.NPJ Microgravity. 2025 Jul 18;11(1):44. doi: 10.1038/s41526-025-00508-6. NPJ Microgravity. 2025. PMID: 40681531 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Prognostic Immune Biomarkers of Overall Survival in Ovarian Cancer Through Comprehensive Bioinformatics Analysis: A Novel Artificial Intelligence Survival Prediction System.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 May 24;8:587496. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.587496. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34109184 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

