Correlation between impulse oscillometry parameters and asthma control in an adult population
- PMID: 31410030
- PMCID: PMC6643487
- DOI: 10.2147/JAA.S193744
Correlation between impulse oscillometry parameters and asthma control in an adult population
Abstract
Purpose: Impulse oscillometry (IOS) has been proposed as an alternative test to evaluate the obstruction of small airways and to detect changes in airways earlier than spirometry. In this study, we sought to determine the utility and association of IOS parameters with spirometry and asthma control in an adult population. Patients and methods: Adults 14-82 years of age with asthma were classified into uncontrolled asthma (n=48), partially controlled asthma (n=45), and controlled asthma (n=49) groups, and characterized with fractional exhaled nitric oxide (FENO), IOS, and spirometry in a transversal analysis planned as a one-visit study. The basic parameters evaluated in IOS are resistance at 5 Hz (R5), an index affected by the large and small airway; resistance at 20 Hz (R20), an index of the resistance of large airways; difference between R5 and R20 (R5-R20), indicative of the function of the small peripheral airways; reactance at 5 Hz (X5), indicative of the capacitive reactance in the small peripheral airways; resonance frequency (Fres), the intermediate frequency at which the reactance is null, and reactance area (XA), which represents the total reactance (area under the curve) at all frequencies between 5 Hz to Fres. Results: There were statistical differences between groups in standard spirometry and IOS parameters reflecting small peripheral airways (R5, R10, R5-R20, Fres, XA and X5) (P<0.001). Accuracy of IOS and/or spirometry to discriminate between controlled asthma vs partially controlled asthma and uncontrolled asthma was low (AUC=0.61). Using linear regression models, we found a good association between spirometry and IOS. In order to evaluate IOS as an alternative or supplementary method for spirometry, we designed a predictive model for spirometry from IOS applying a penalized regression model (Lasso). Then, we compared the original spirometry values with the values obtained from the predictive model using Bland-Altman plots, and the models showed an acceptable bias in the case of FEV1/FVC, FEV1%, and FVC%. Conclusion: IOS did not show a discriminative capacity to correctly classify patients according to the degree of asthma control. However, values of IOS showed good association with values of spirometry. IOS could be considered as an alternative and accurate complement to spirometry in adults. In a predictive model, spirometry values estimated from IOS tended to overestimate in low values of "real" spirometry and underestimate in high values.
Keywords: asthma; lung function tests; oscillometry; spirometry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

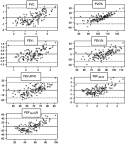
Similar articles
-
Relating small airways to asthma control by using impulse oscillometry in children.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012 Mar;129(3):671-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2011.11.002. Epub 2011 Dec 17. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22178635 Free PMC article.
-
"Reactance inversion" at low frequencies during lung function measurement by impulse oscillometry in children with persistent asthma.J Asthma. 2022 Aug;59(8):1597-1603. doi: 10.1080/02770903.2021.1955376. Epub 2021 Aug 6. J Asthma. 2022. PMID: 34255601
-
Application Value of Broadband 3-Dimensional Impulse Oscillometry in COPD.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021 Feb 4;16:215-223. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S285927. eCollection 2021. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2021. PMID: 33574662 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Value of Impulse Oscillometry in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Respiration. 2025;104(2):100-109. doi: 10.1159/000541633. Epub 2024 Oct 3. Respiration. 2025. PMID: 39362193
-
The case for impulse oscillometry in the management of asthma in children and adults.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017 Jun;118(6):664-671. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2017.04.009. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28583260 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
D-ROMs and PAT Tests Reveal a High Level of Oxidative Stress in Patients with Severe Well-Controlled Asthma, and D-ROMs Are Positively Correlated with R20 Values That Indicate Approximate Central Airway Resistance.J Pers Med. 2023 Jun 2;13(6):943. doi: 10.3390/jpm13060943. J Pers Med. 2023. PMID: 37373932 Free PMC article.
-
Detection of Inadequately Controlled Asthma in Adults Using Impulse Oscillometry and Fractional Exhaled Nitric Oxide.J Asthma Allergy. 2025 Apr 25;18:637-647. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S516257. eCollection 2025. J Asthma Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40308752 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Impulse Oscillometry in Evaluating Disease Severity and Predicting the Airway Reversibility in Patients With Bronchiectasis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 25;9:796809. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.796809. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 36687424 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of Forced Oscillatory Technique in Obstructive and Restrictive Pulmonary Diseases: A Concise State of the Art.J Clin Med. 2025 Aug 12;14(16):5718. doi: 10.3390/jcm14165718. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40869544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lifetime cannabis exposure and small airway function in a population-based cohort study.ERJ Open Res. 2022 May 3;8(2):00688-2021. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00688-2021. eCollection 2022 Apr. ERJ Open Res. 2022. PMID: 35509440 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Teeter JG, Bleecker ER. Relationship between airway obstruction and respiratory symptoms in adult asthmatics. Chest. 1998;113:272–277. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

