Interstitial Lung Disease in a Patient Treated with Denosumab
- PMID: 31410352
- PMCID: PMC6663050
- DOI: 10.12890/2019_001131
Interstitial Lung Disease in a Patient Treated with Denosumab
Abstract
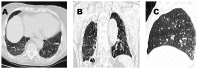
Denosumab is an antiresorptive agent widely used for treating osteoporosis. Atypical femur fractures, osteonecrosis of the jaw and hypocalcaemia are well-known possible adverse effects of this drug. We present, to our knowledge, the first case report in the English literature of clinically significant interstitial lung disease likely related to denosumab.
Learning points: Denosumab is a fully human monoclonal antibody which may rarely cause interstitial lung disease (ILD).The findings from this isolated case report of ILD in a patient taking denosumab do not prove causality.Nevertheless, we suggest that patient exposure to denosumab should be considered in a patient with ILD.
Keywords: Interstitial lung disease; denosumab; osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interests: The Authors declare that there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Cummings SR, San Martin J, McClung MR, et al. Denosumab for prevention of fractures in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:756–765. - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Zhang X. Receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand (RANKL)/RANK/osteoprotegerin system in bone and other tissues. Mol Med Rep. 2015;11:3212–3218. - PubMed
-
- Boorsma C, Draijer C, Cool R, et al. The RANKL-OPG balance in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. 2015;46:PA3809.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
