Quantification of ractopamine residues on and in beef digestive tract tissues
- PMID: 31410462
- PMCID: PMC6776262
- DOI: 10.1093/jas/skz263
Quantification of ractopamine residues on and in beef digestive tract tissues
Abstract
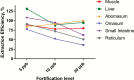
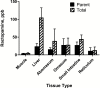
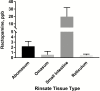
Ractopamine hydrochloride is a commercial beta-adrenergic agonist commonly used as a dietary supplement in cattle production for improved feed efficiency and growth promotion. Currently, regulatory target tissues (as approved in the New Animal Drug Application with Food and Drug Administration) for ractopamine residue testing are muscle and liver. However, other tissues have recently been subjected to testing in some export markets for U.S. beef, a clear disregard for scientific maximum residue limits associated with specific tissues. The overall goal of this study was to develop and validate an LC-MS/MS assay to determine whether detectable and quantifiable levels of ractopamine in digestive tract-derived edible offal items (i.e., abomasum, omasum, small intestine, and reticulum) of cattle resulted from tissue residues or residual ingesta contamination of exposed surfaces of tissues (rinsates). Tissue samples and corresponding rinsates from 10 animals were analyzed for parent and total ractopamine (tissue samples only). The lower limit of quantitation was between 0.03 and 0.66 ppb depending on the tissue type, and all tissue and rinsate samples tested had quantifiable concentrations of ractopamine. The highest concentrations of tissue-specific ractopamine metabolism (represented by higher total vs. parent ractopamine levels) were observed in liver and small intestine. Contamination from residual ingesta (represented by detectable ractopamine in rinsate samples) was only detected in small intestine, with a measured mean concentration of 19.72 ppb (±12.24 ppb). Taken together, these results underscore the importance of the production process and suggest that improvements may be needed to reduce the likelihood of contamination from residual ractopamine in digestive tract-derived edible offal tissues for market.
Keywords: beef; export; offal tissue; ractopamine; residue.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the American Society of Animal Science. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of differing withdrawal times from ractopamine hydrochloride on residue concentrations of beef muscle, adipose tissue, rendered tallow, and large intestine.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 2;15(12):e0242673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242673. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33264353 Free PMC article.
-
Tissue residues of ractopamine and urinary excretion of ractopamine and metabolites in animals treated for 7 days with dietary ractopamine.J Anim Sci. 2002 May;80(5):1240-9. doi: 10.2527/2002.8051240x. J Anim Sci. 2002. PMID: 12019611
-
Liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem mass spectrometric analysis of incurred ractopamine residues in livestock tissues.Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2002;16(13):1261-5. doi: 10.1002/rcm.717. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom. 2002. PMID: 12112252
-
[About the human health safety estimation of ractopamine intake together with the food].Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2013;(6):4-8. doi: 10.15690/vramn.v68i6.666. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 2013. PMID: 24340628 Review. Russian.
-
Ractopamine residues in meat might reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes.Nutr Health. 2023 Mar;29(1):5-7. doi: 10.1177/02601060221108146. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Nutr Health. 2023. PMID: 35702043 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of differing withdrawal times from ractopamine hydrochloride on residue concentrations of beef muscle, adipose tissue, rendered tallow, and large intestine.PLoS One. 2020 Dec 2;15(12):e0242673. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0242673. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33264353 Free PMC article.
-
Sample Preparation Techniques for Growth-Promoting Agents in Various Mammalian Specimen Preceding MS-Analytics.Molecules. 2024 Jan 9;29(2):330. doi: 10.3390/molecules29020330. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38257243 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anderson D. B., Moody D. E., and Hancock D. L.. . 2004. Beta adrenergic agonists. In: Pond W. G. and Bell A. W., editors. Encyclopedia of animal science. New York (NY): Marcel Dekker, Inc, p. 104–107.
-
- AOAC 2015. Setting global standards. http://www.aoac.org/aoac_prod_imis/AOAC/AOAC_Member/AOACACF/AOACOCF/AOA... Accessed April 17, 2019.
-
- Bories G., Brantom P., de Barbera J. B., Chesson A., Cocconcelli P. S., Debski B., Dierick N., Gropp J., Halle I., Hogstrand C., . et al. 2009. Safety evaluation of ractopamine. EFSA J. 1041:1–52. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2009.1041. - DOI
-
- Burnett T. J., Rodewald J. M., Brunelle S. L., Neeley M., Wallace M., Connolly P., and Coleman M. R.. . 2012. Determination and confirmation of parent and total ractopamine in bovine, swine, and turkey tissues by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry: First Action 2011.23. J. AOAC Int. 95:1235–1255. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

