Health state utility values (QALY weights) for Huntington's disease: an analysis of data from the European Huntington's Disease Network (EHDN)
- PMID: 31410669
- PMCID: PMC6856291
- DOI: 10.1007/s10198-019-01092-9
Health state utility values (QALY weights) for Huntington's disease: an analysis of data from the European Huntington's Disease Network (EHDN)
Abstract
Background: Huntington's Disease (HD) is a hereditary neurodegenerative disorder which affects individuals' ability to walk, talk, think, and reason. Onset is usually in the forties, there are no therapies currently available that alter disease course, and life expectancy is 10-20 years from diagnosis. The gene causing HD is fully penetrant, with a 50% probability of passing the disease to offspring. Although the impacts of HD are substantial, there has been little report of the quality of life of people with the condition in a manner that can be used in economic evaluations of treatments for HD. Health state utility values (HSUVs), used to calculate quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs), are the metric commonly used to inform such healthcare policy decision-making.
Objectives: The aim was to report HSUVs for HD, with specific objectives to use European data to: (i) describe HSUVs by demographic and clinical characteristics; (ii) compare HSUVs of people with HD in the UK with population norms; (iii) identify the relative strength of demographic and clinical characteristics in predicting HSUVs.
Methods: European Huntington's Disease Network REGISTRY study data were used for analysis. This is a multi-centre, multi-national, observational, longitudinal study, which collects six-monthly demographic, clinical, and patient-reported outcome measures, including the SF-36. SF-36 scores were converted to SF-6D HSUVs and described by demographic and clinical characteristics. HSUVs from people with HD in the UK were compared with population norms. Regression analysis was used to estimate the relative strength of age, gender, time since diagnosis, and disease severity (according to the Total Function Capacity (TFC) score, and the UHDRS's Motor score, Behavioural score, and Cognition score) in predicting HSUVs.
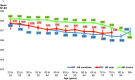
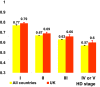
Results: 11,328 questionnaires were completed by 5560 respondents with HD in 12 European countries. Women generally had lower HSUVs than men, and HSUVs were consistently lower than population norms for those with HD in the UK, and dropped with increasing disease severity. The regression model significantly accounted for the variance in SF-6D scores (n = 1939; F [7,1931] = 120.05; p < 0.001; adjusted R-squared 0.3007), with TFC score, Behavioural score, and male gender significant predictors of SF-6D values (p < 0.001).
Conclusion: To our knowledge, this is the first report of HSUVs for HD for countries other than the UK, and the first report of SF-6D HSUVs described for 12 European countries, according to demographic and clinical factors. Our analyses provide new insights into the relationships between HD disease characteristics and assessment of health-related quality of life in a form that can be used in policy-relevant economic evaluations.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness analysis; Health state utility values; Huntington’s disease; Quality-adjusted life-years.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Health Utilities for Multiple Sclerosis.Value Health. 2016 Jun;19(4):460-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2016.01.002. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Value Health. 2016. PMID: 27325338
-
Systematic Review of Health State Utility Values Used in European Pharmacoeconomic Evaluations for Chronic Hepatitis C: Impact on Cost-Effectiveness Results.Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2021 Jan;19(1):29-44. doi: 10.1007/s40258-020-00600-w. Appl Health Econ Health Policy. 2021. PMID: 32661846
-
Identification of genetic variants associated with Huntington's disease progression: a genome-wide association study.Lancet Neurol. 2017 Sep;16(9):701-711. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(17)30161-8. Epub 2017 Jun 20. Lancet Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28642124
-
Exploring health state utility values of parents of children with a serious illness.Qual Life Res. 2020 Jul;29(7):1947-1959. doi: 10.1007/s11136-020-02466-w. Epub 2020 Apr 25. Qual Life Res. 2020. PMID: 32335816
-
NICE DSU Technical Support Document 12: The Use of Health State Utility Values in Decision Models [Internet].London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2011 Jul. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE); 2011 Jul. PMID: 28481493 Free Books & Documents. Review.
Cited by
-
Humanistic Burden of Huntington Disease: Evidence From the Huntington Disease Burden of Illness Study.Neurol Clin Pract. 2022 Dec;12(6):e172-e180. doi: 10.1212/CPJ.0000000000200095. Neurol Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 36540140 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive pharmacological treatment in subjects at risk for fatal familial insomnia: science and public engagement.Prion. 2022 Dec;16(1):66-77. doi: 10.1080/19336896.2022.2083435. Prion. 2022. PMID: 35737759 Free PMC article.
-
Two Decades of Huntington's Disease in Varna, Bulgaria: A Retrospective Single-Centre Study of Clinical Trends and Challenges.Neurol Int. 2025 Jun 18;17(6):95. doi: 10.3390/neurolint17060095. Neurol Int. 2025. PMID: 40559333 Free PMC article.
-
SUMO-modifying Huntington's disease.IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022 Mar 9;12:203-209. doi: 10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.03.002. eCollection 2022 Jun. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35746980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychometric Properties and Validation of the Polish Version of the 12-Item World Health Organization Disability Assessment Schedule 2.0 in Patients with Huntington's Disease.J Clin Med. 2021 Mar 4;10(5):1053. doi: 10.3390/jcm10051053. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33806307 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical