Heterogeneity in the aetiology of diabetes mellitus in young adults: A prospective study from north India
- PMID: 31411171
- PMCID: PMC6676834
- DOI: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1004_17
Heterogeneity in the aetiology of diabetes mellitus in young adults: A prospective study from north India
Abstract
Background & objectives: In contrast to Caucasians of European origin, the aetiology of diabetes mellitus (DM) in young adults in other ethnic groups, including Indians is likely to be heterogeneous and difficult to determine. This study was undertaken to determine the aetiology of diabetes in young Indian adults using a protocol-based set of simple clinical and investigation tools.
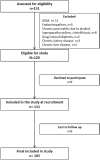
Methods: In this prospective study, 105 Indian young adults with diabetes (age at onset 18-35 yr; duration <2 yr) were studied for a period of 1-3 years. Pancreatic imaging, fasting C-peptide, islet antibodies (against glutamic acid decarboxylase, tyrosine phosphatase and zinc transporter-8) and mitochondrial A3243G mutational analysis were performed in all patients. Four patients were screened for maturity-onset diabetes of the young (MODY) using next-generation sequencing.
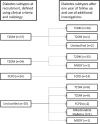
Results: Type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T1DM and T2DM) were equally frequent (40% each), followed by fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes (FCPD, 15%). Less common aetiologies included MODY (2%), mitochondrial diabetes (1%) and Flatbush diabetes (2%). There was considerable phenotypic overlap between the main aetiological subtypes. Elevated islet antibodies were noted in 62 per cent of T1DM patients [positive predictive value (PPV) 84%; negative predictive value (NPV) 78%] while low plasma C-peptide (<250 pmol/l) was present in 56 per cent of T1DM patients [PPV 96% (after excluding FCPD), NPV 72%]. Using these tests and observing the clinical course over one year, a final diagnosis was made in 103 (99%) patients, while the diagnosis at recruitment changed in 23 per cent of patients.
Interpretation & conclusions: The aetiology of diabetes in young adults was heterogeneous, with T1DM and T2DM being equally common. FCPD was also frequent, warranting its screening in Indian patients. Testing for islet antibodies and C-peptide in this age group had good PPV for diagnosis of T1DM.
Keywords: Aetiological heterogeneity; C-peptide; early-onset diabetes; fibrocalculous pancreatic diabetes; islet antibodies.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


Comment in
-
Young-onset diabetes: An Indian perspective.Indian J Med Res. 2019 Apr;149(4):441-442. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_1938_18. Indian J Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31411167 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alberti G, Zimmet P, Shaw J, Bloomgarden Z, Kaufman F, Silink M, et al. Type 2 diabetes in the young: The evolving epidemic: The International Diabetes Federation consensus workshop. Diabetes Care. 2004;27:1798–811. - PubMed
-
- Shaw JE, Sicree RA, Zimmet PZ. Global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2010;87:4–14. - PubMed
-
- Laakso M, Pyörälä K. Age of onset and type of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1985;8:114–7. - PubMed
-
- Borg H, Arnqvist HJ, Björk E, Bolinder J, Eriksson JW, Nyström L, et al. Evaluation of the new ADA and WHO criteria for classification of diabetes mellitus in young adult people (15-34 yrs) in the diabetes incidence study in Sweden (DISS) Diabetologia. 2003;46:173–81. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
